MAAP #149: Mennonite Colonies Continue Major Deforestation in Peruvian Amazon

The Mennonites, a religious group often associated with agricultural activity, have become one of the major deforestation drivers in the Peruvian Amazon.
In October 2020, we reported the deforestation of over 3,400 hectares across three new colonies established.
Here, we show that in 2021 the Mennonites have established a fourth colony (over 400 hectares) and continued expansion of the first three colonies.
In total, we have now documented the deforestation of 3,968 hectares (9,805 acres) across four new colonies established in the Peruvian Amazon since 2017, making it the new leading cause of large-scale deforestation in Peru.
Moreover, there are strong indications that much of this deforestation is illegal (see MAAP #127).
Below, we present the following:
- An updated Base Map showing the location of the four new Mennonite colonies in the Peruvian Amazon.
p - A series of satellite images showing the most recent deforestation in the newest colony (referred to here as “Padre Marquez”).
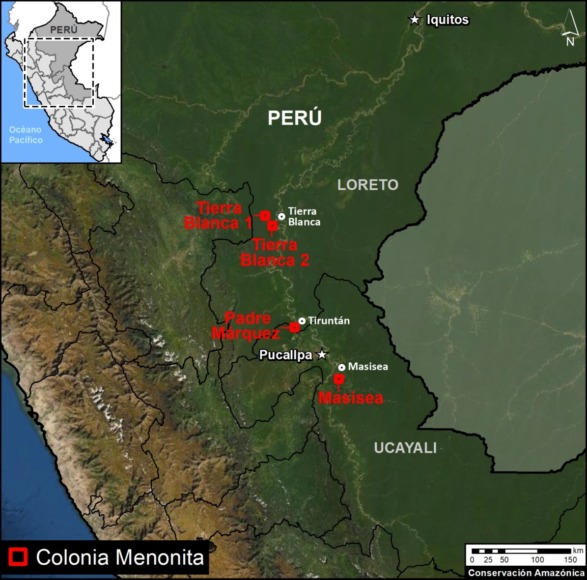
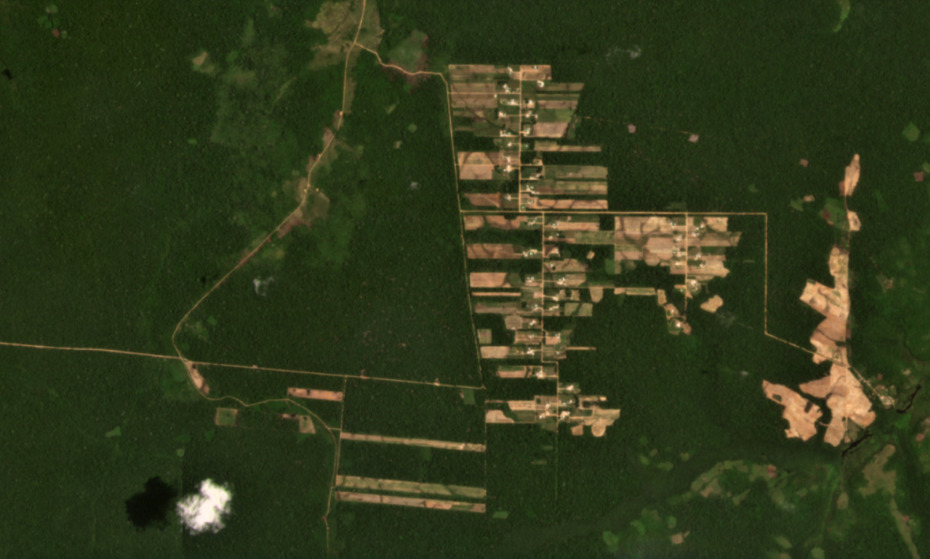
Updated Base Map showing the location of the four major new Mennonite Colonies in the Peruvian Amazon. Data: MAAP.
Base Map
The Base Map shows the location of the four major Mennonite colonies in the Peruvian Amazon.
The newest colony is referred to here as “Padre Marquez,” named for a nearby town. Note that it is located about halfway between the other colonies (Tierra Blanca to the north and Masisea to the south.
Of the total deforestation (3,968 hectares):
- 66% (2,628 ha) is in the Tierra Blanca colonies in Loreto;
- 23% (918 ha) is in Masisea colony in Ucayali;
- 11% (421) is in the new Padre Marquez colony along the Ucayali/Loreto border.
k - 12% occurred in 2021 (495 ha). In addition to the establishment of Padre Marquez, we also detected expansion in the Tierra Blanca and Masisea colonies.
Deforestation 2021
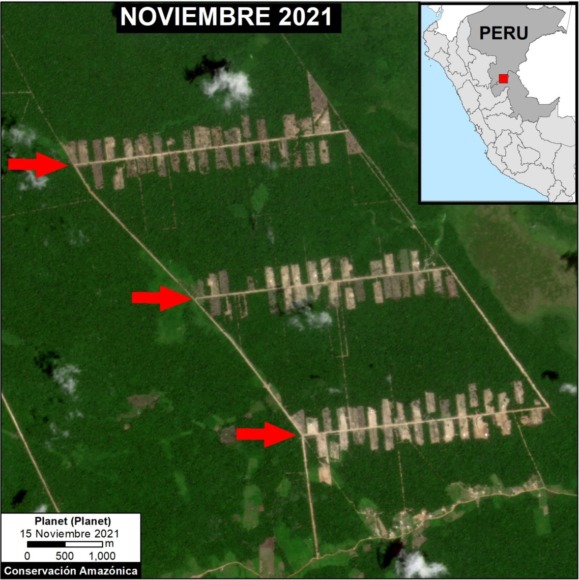
The following image shows the large-scale deforestation of 366 hectares between January (left panel) and November (right panel) 2021 associated with the main section of the new Padre Marquez colony. The red arrows serve as reference points between the two panels. Click to enlarge.
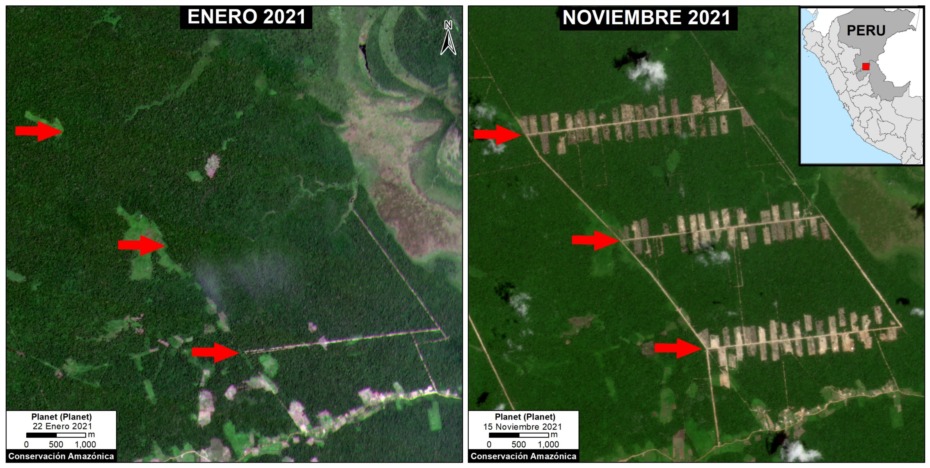
Deforestation between January (left panel) and November 2021 (right panel), associated with the new Padre Marquez colony. Data: Planet, MAAP. Click to enlarge.
Satellite Images of Each Mennonite Colony
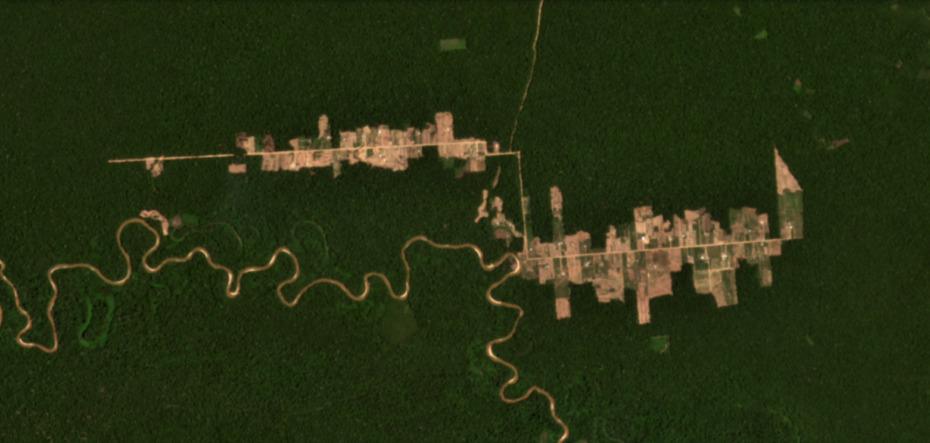
Tierra Blanca 1
The following image shows the deforestation of 2,200 hectares (5,436 acres) since 2017 in the Tierra Blanca 1 colony (Loreto region). In 2021, this deforestation mostly stopped (only 8 ha).
Tierra Blanca 2
The following image shows the additional deforestation of 428 hectares (1,058 acres) in the nearby Tierra Blanca s colony (Loreto region). In 2021, this deforestation also mostly stopped (15 ha).
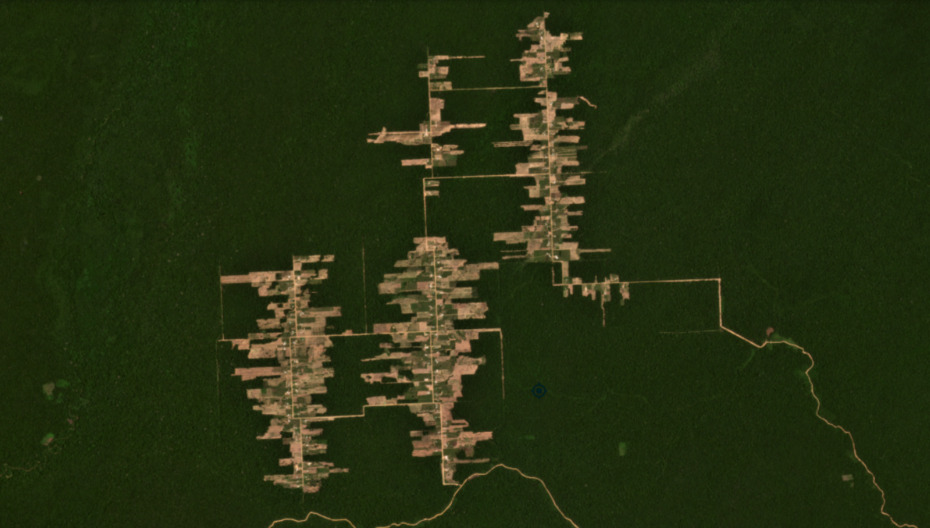
Masisea
The following image shows the deforestation of 918 hectares (2,268 acres) in the Masisea colony (Ucayali region). In 2021, there was a major expansion to the east (with 47 ha of new deforestation).
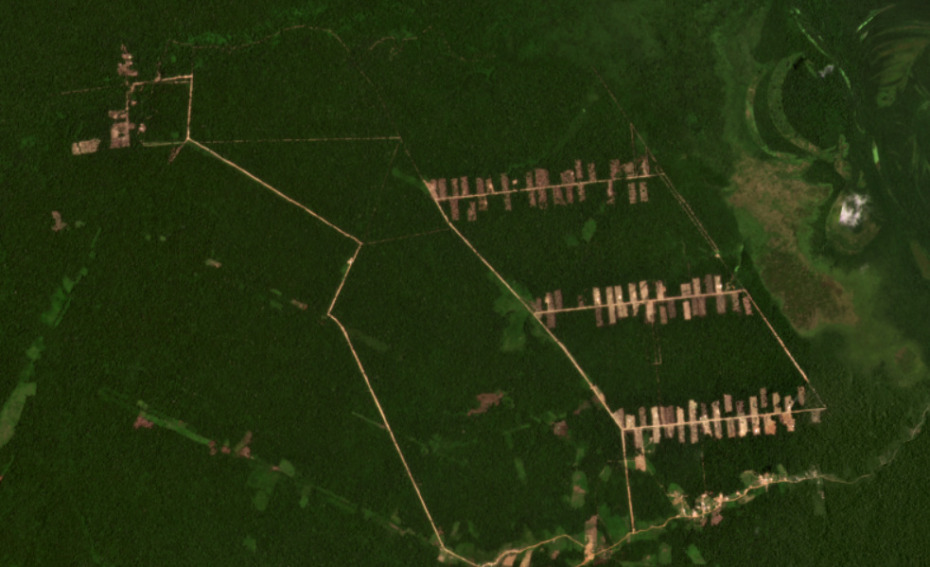
Padre Marquez
The following image shows the deforestation of 421 hectares (1,040 acres) in the Padre Marquez colony (Ucayali region), all of which occured in 2021.
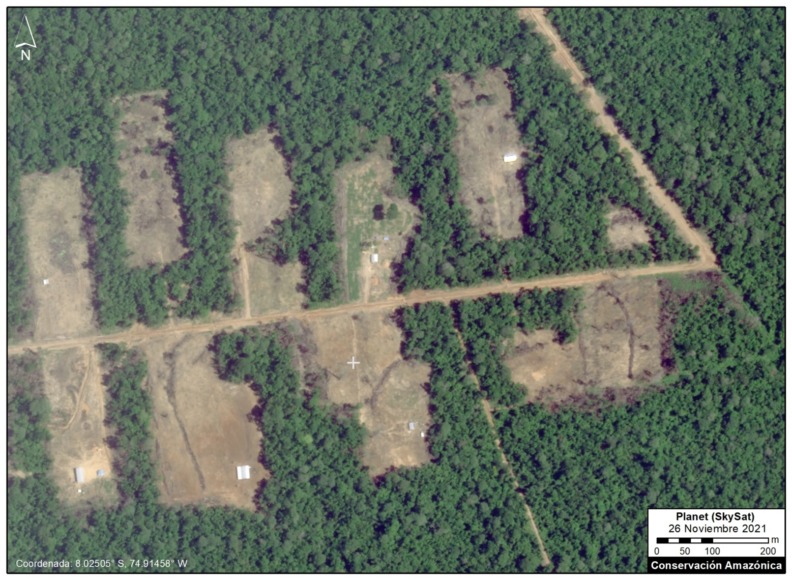
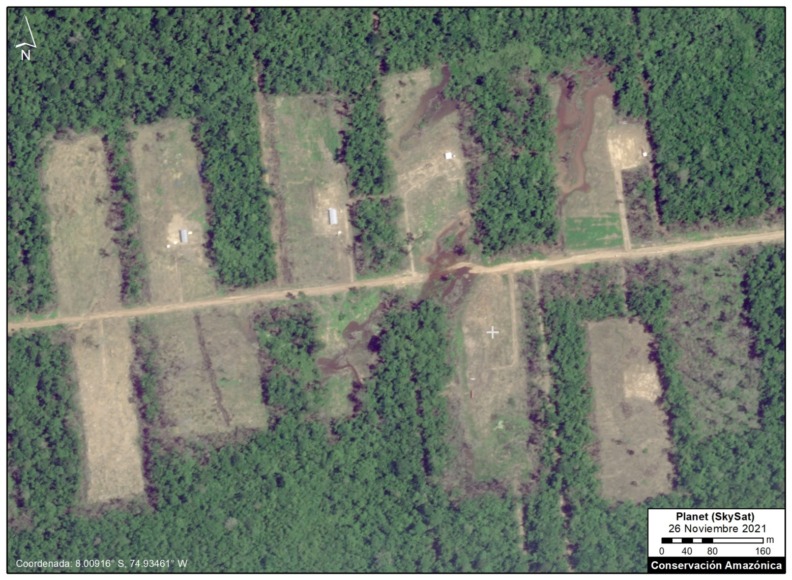
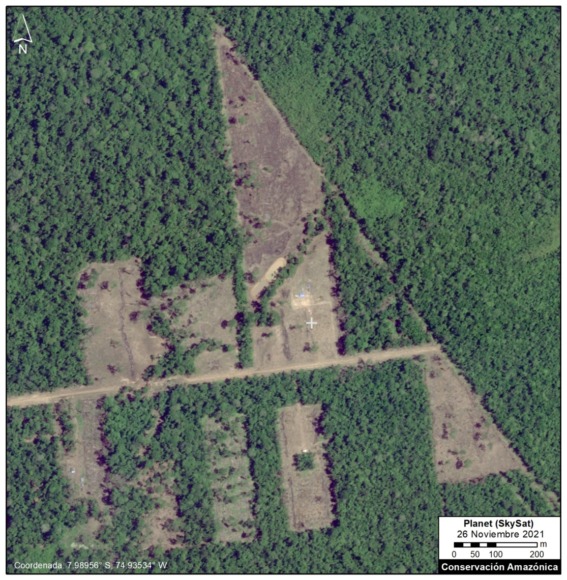
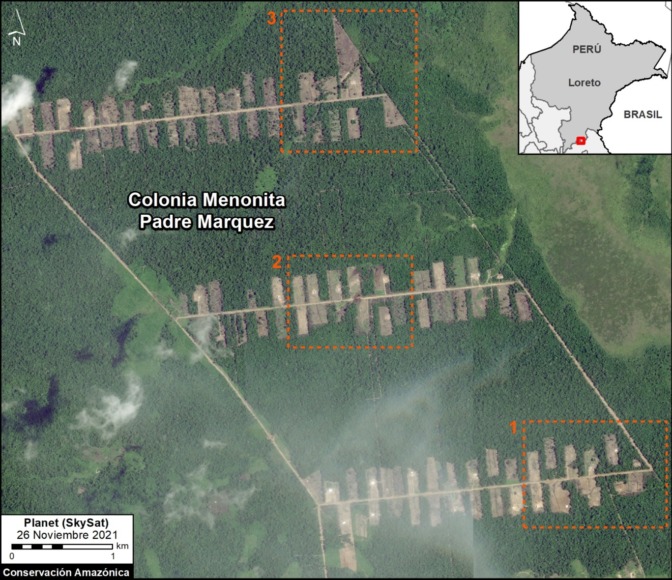
Very High-Resolution Images of Padre Marquez colony
Below, we present a series of very high resolution (0.5 meter) satellite images of the Padre Marquez colony, thanks to the company Planet and their Skysat fleet. The image allows enhanced visualization of some details of the deforested area, such as roads, buildings, and cleared land for likely agricultural activities. Click to enlarge.
Declaration from the Peruvian Ministry of Environment (MINAM):
La destrucción de cientos de hectáreas de bosques en Loreto y en Ucayali causada por las ocupaciones irregulares de colonias menonitas, ha sido priorizada por el MINAM a través de las siguientes acciones:
1. Denuncias penales por afectación de las formaciones boscosas, contra los dirigentes de las colonias menonitas. Cuatro denuncias en Ucayali y una denuncia penal en Loreto.
2. Medidas cautelares, en el marco de las denuncias penales, para que la autoridad judicial disponga la suspensión de las acciones destructivas y predatorias del bosque.
3. Solicitudes a las entidades de control institucional para la supervisión sobre el ejercicio funcional de las autoridades regionales a cargo del otorgamiento de permisos que afectan el bosque.
4. Además, el MINAM ha venido ejecutando y coordinando diversas acciones con la finalidad que las entidades competentes investiguen, sancionen y paralicen las actividades irregulares de estas personas extranjeras que no solamente han ingresado sin las autorizaciones respectivas para ejecutar actividades económicas, sino que además están dañando ostensiblemente el patrimonio natural peruano.
Acknowledgements
We thank M.E. Gutierrez, E. Ortiz, S. Novoa, R. Catpo, D. Suarez and G. Palacios for helpful comments to earlier versions of this report.
This work was supported by the following major funders: Erol Foundation, Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (NORAD), and International Conservation Fund of Canada (ICFC).
Citation
Finer M, Mamani N, Spore J, Suarez D (2021)Mennonite Colonies Continue Major Deforestation in Peruvian Amazon. MAAP: 149.
Download PDF of this article