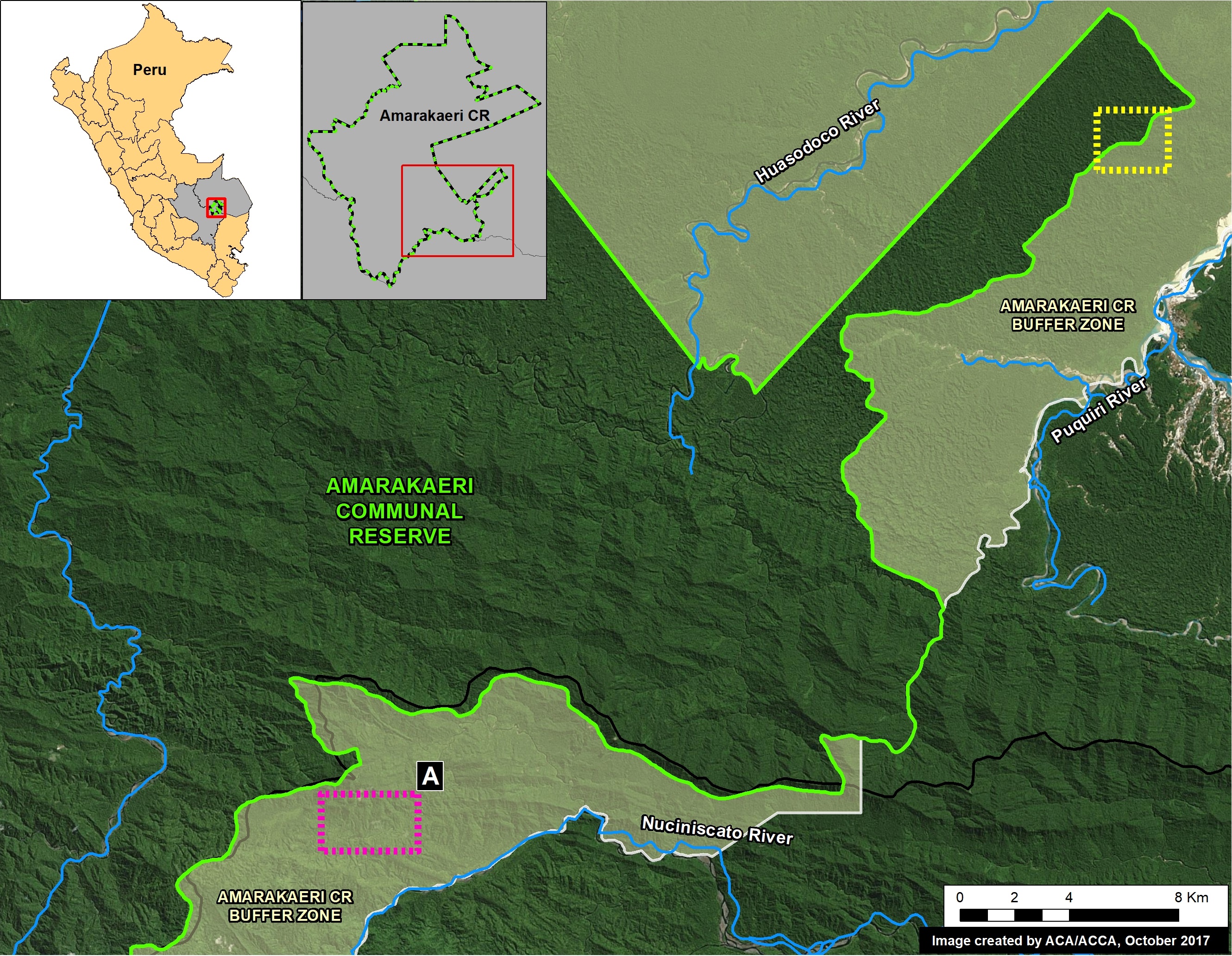
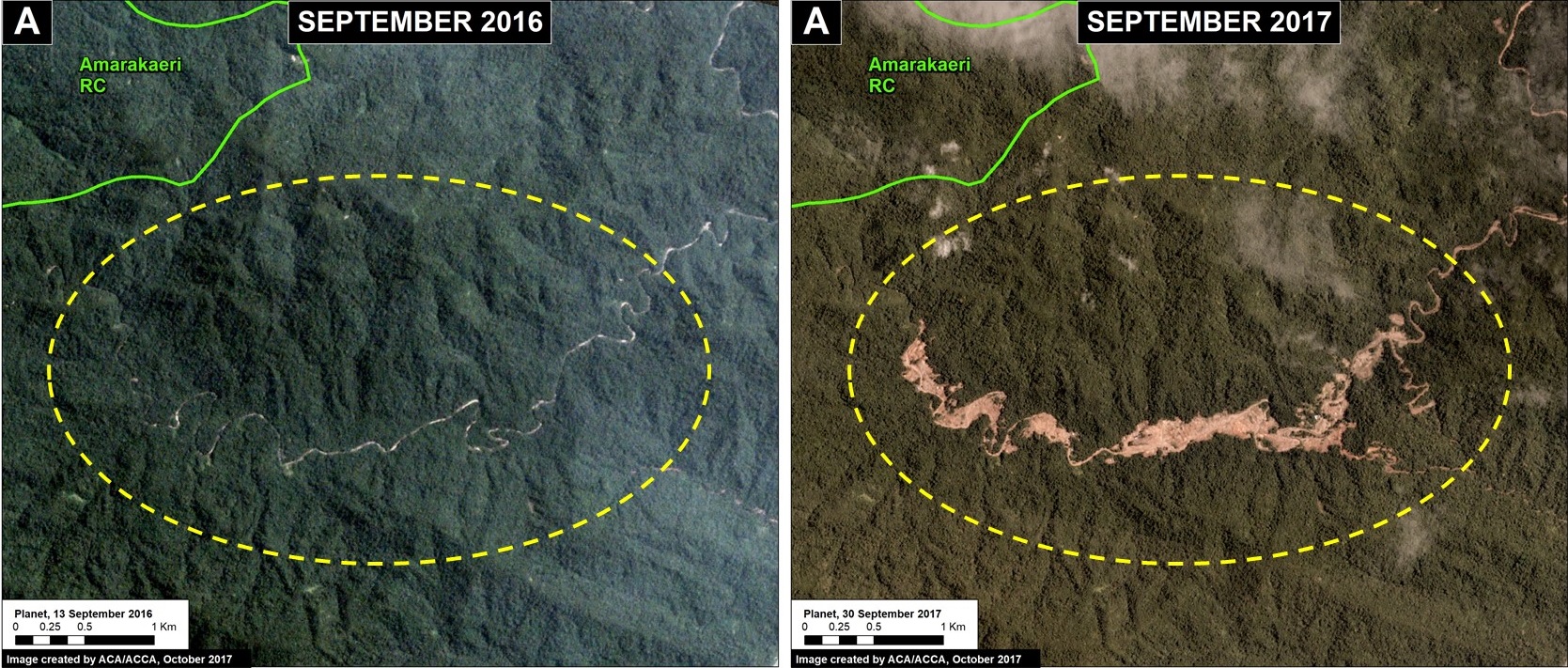
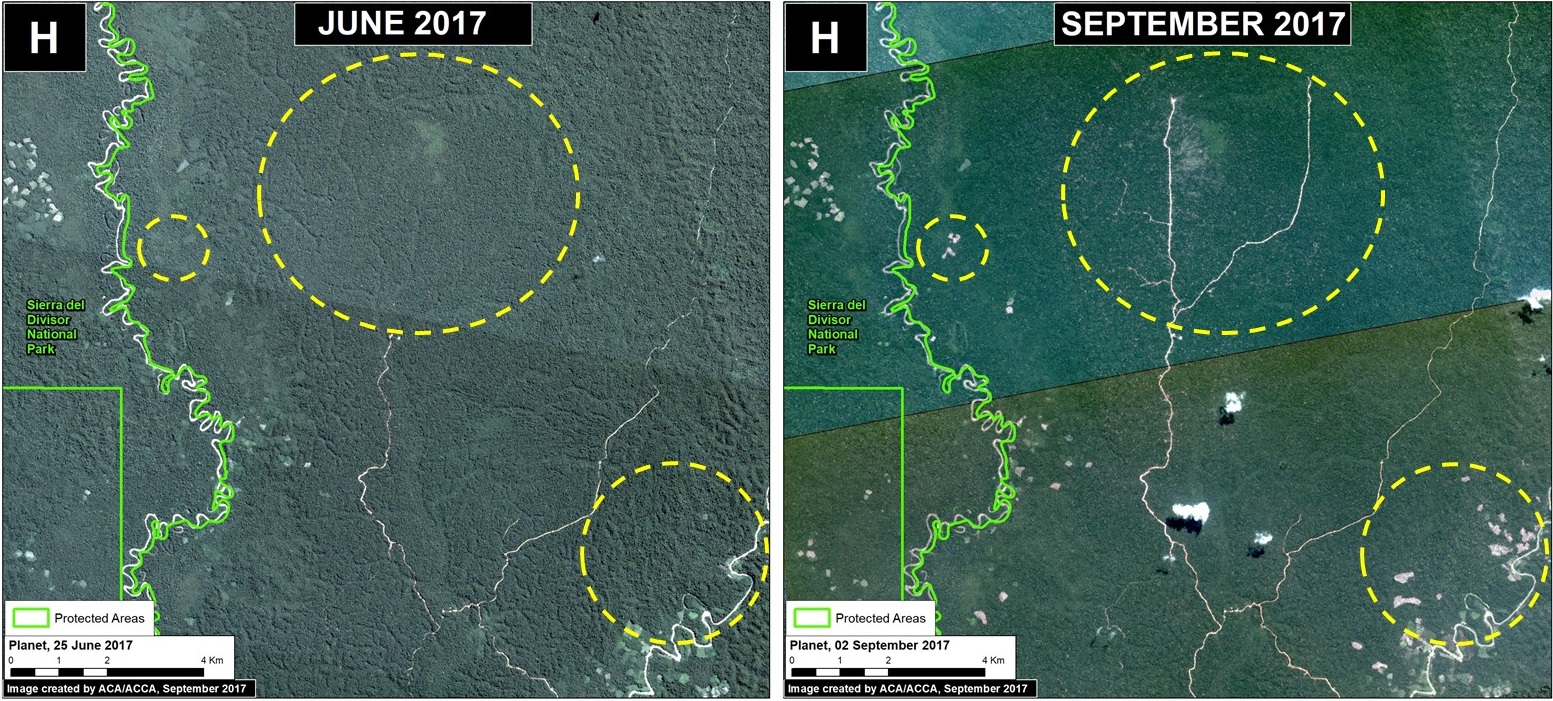
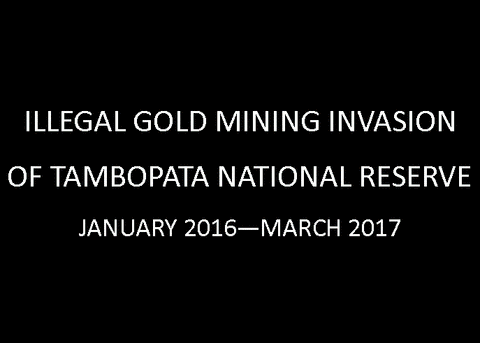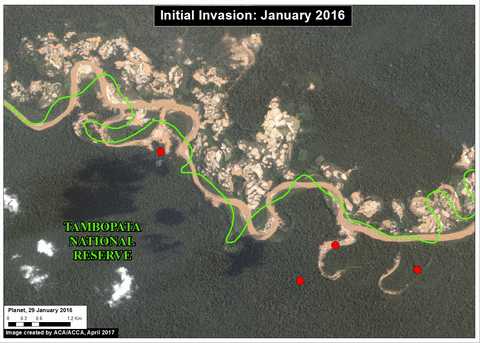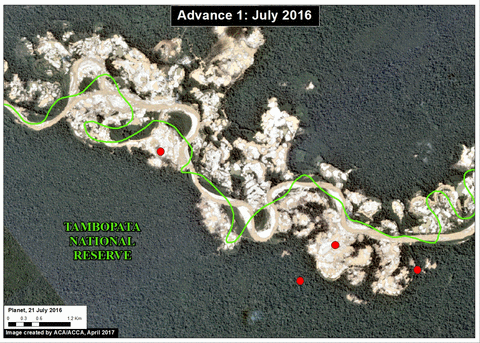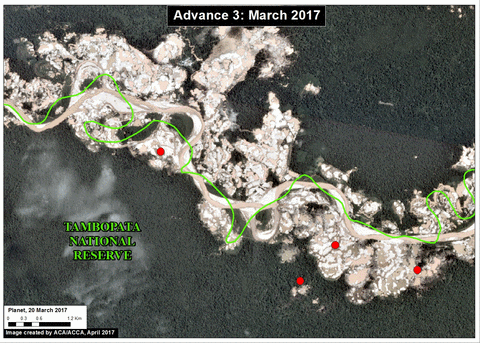Pope Francis, as part of his upcoming visit to Peru in January, will visit the Madre de Dios region in the southern Peruvian Amazon. He is expected to address issues facing the Amazon and its indigenous communities, including deforestation.
In this article, we show that Madre de Dios is experiencing a deforestation crisis, due mainly to impacts from gold mining, small-scale agriculture, and roads.
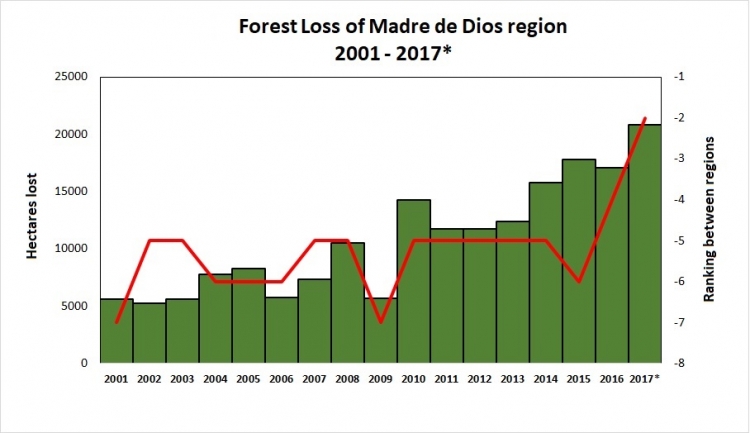
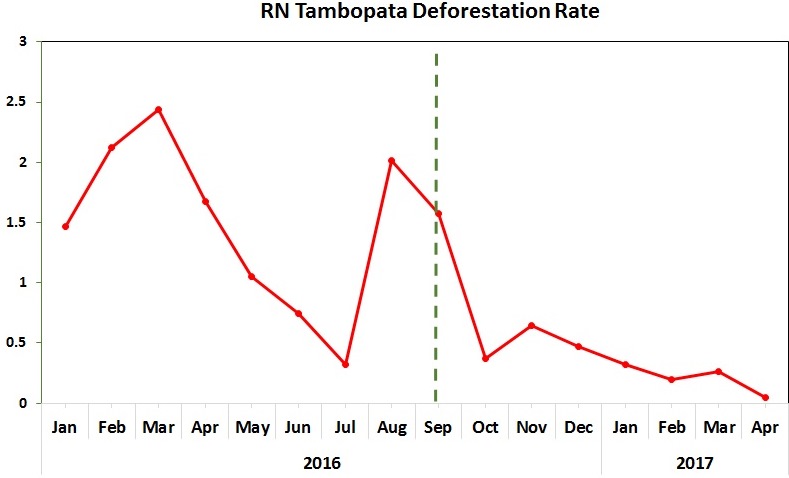
Table 76 shows the increasing trend of annual forest loss since 2001, peaking in 2017. In fact, in 2017 forest loss exceeded 20,000 hectares (49,000 acres) for the first time, doubling the loss in 2008.*
The table also shows the ranking of Madre de Dios in respect to the annual forest loss compared to all other regions of the Peruvian Amazon (see red line). For the first time, Madre de Dios is the region with the second highest forest loss total, behind only Ucayali.
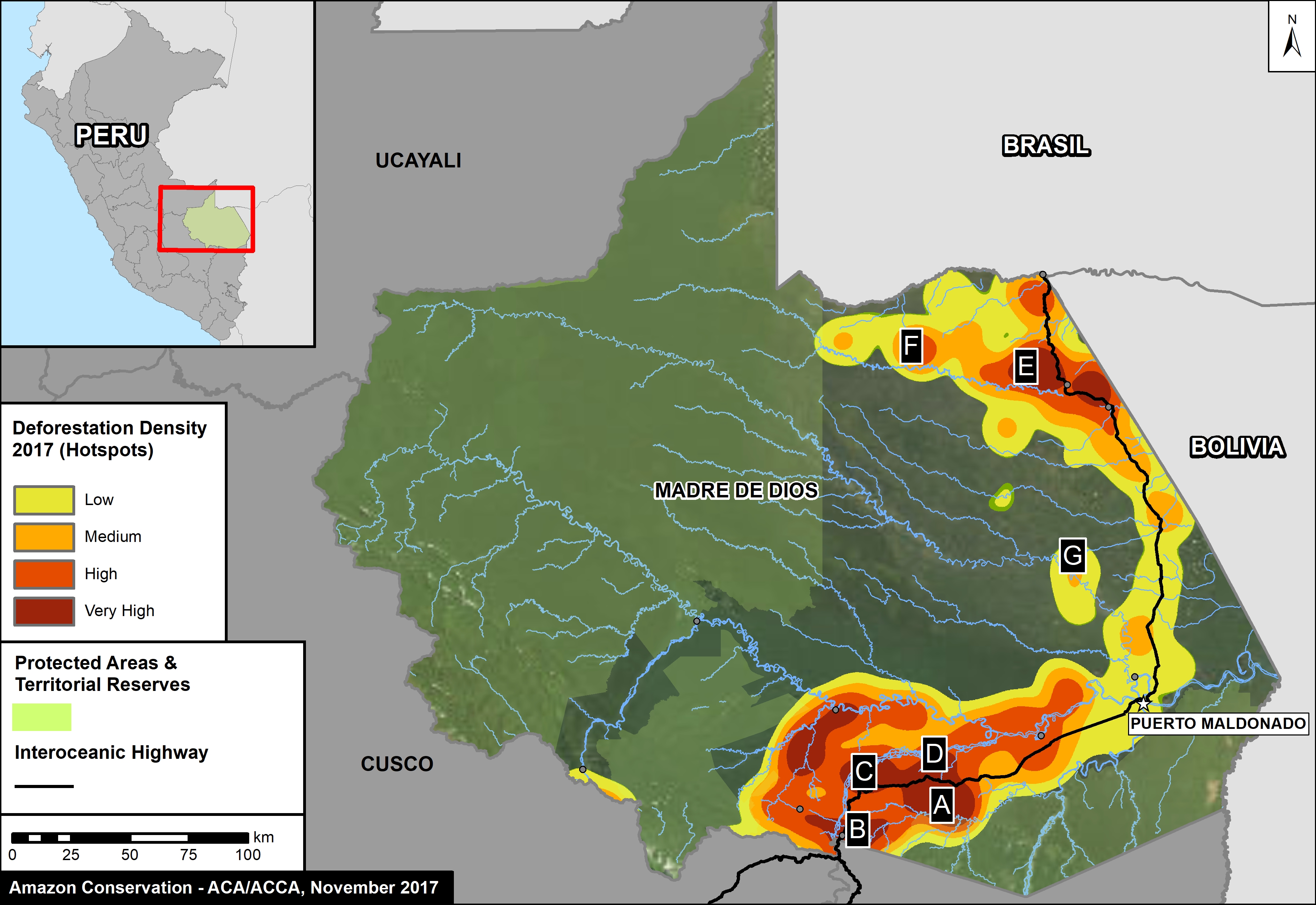
Next, we present a map of deforestation hotspots in Madre de Dios in 2017, along with satellite images of a number of the most intense hotspots.
*The total estimated forest loss in 2017 was based on early warnings alerts generated by the University of Maryland (GLAD alerts) and the Peruvian Environment Ministry (PNCB/MINAM). The estimate is 20,826 hectares as of the first week of November.
Deforestation Hotspots in Madre de Dios
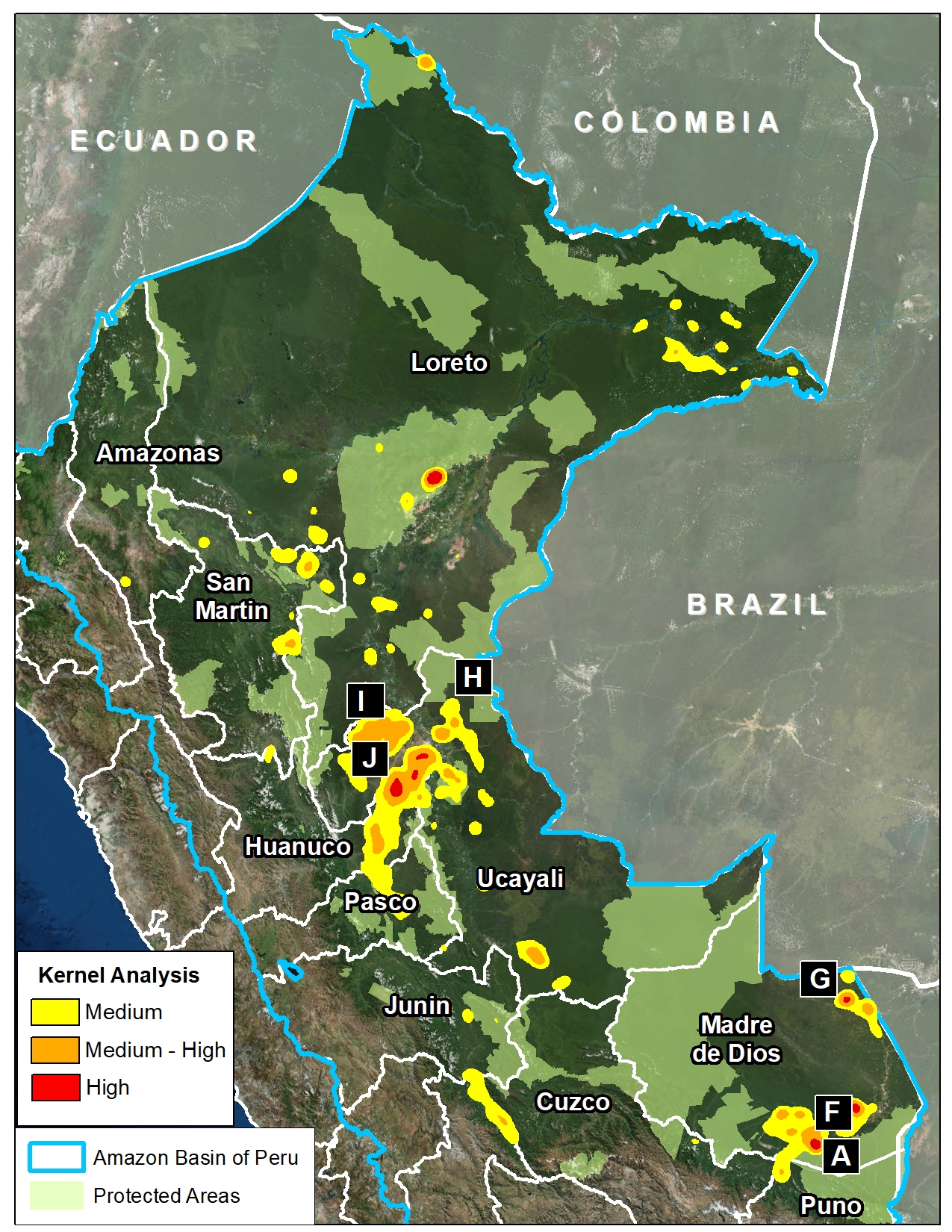
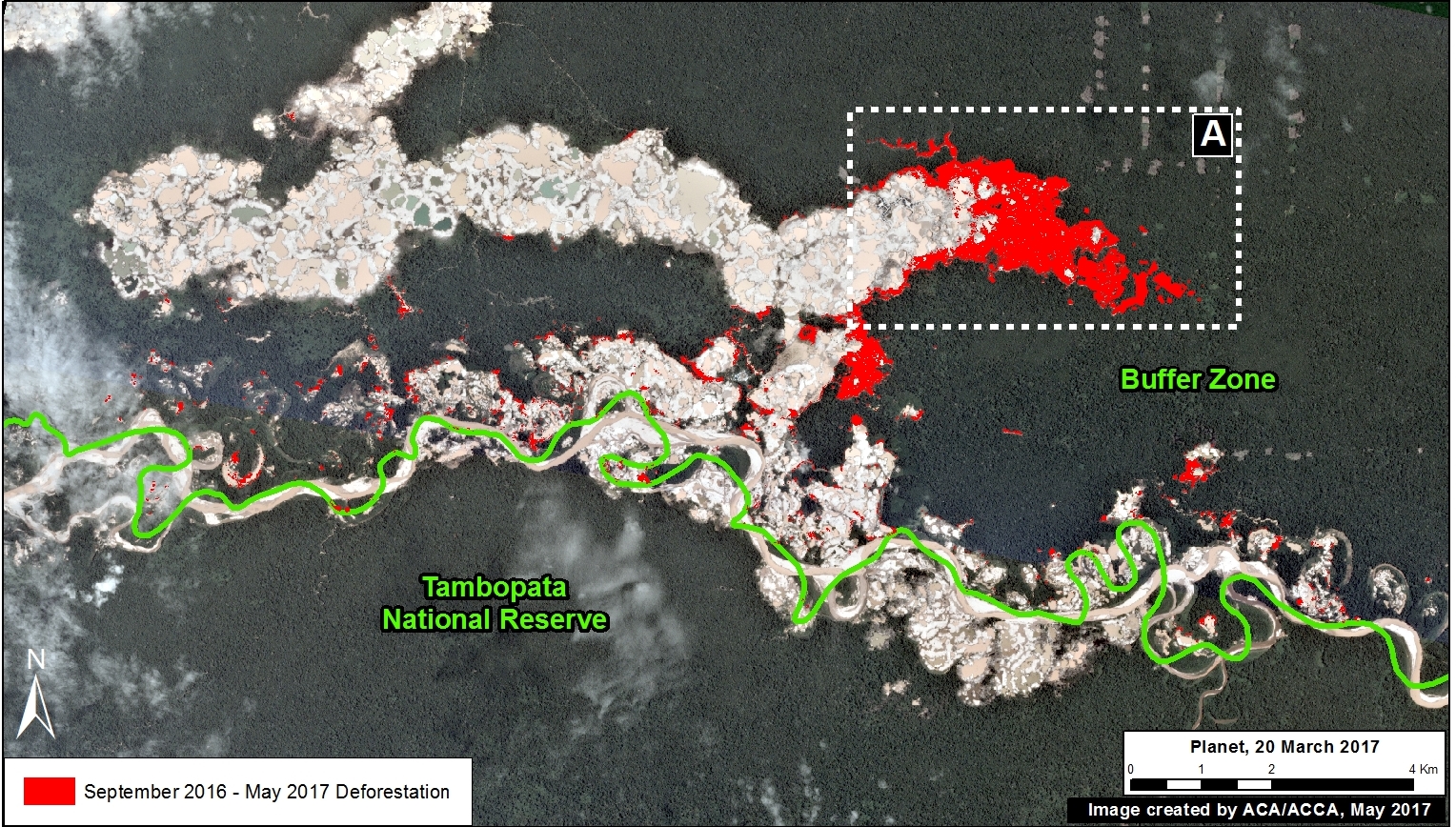
Image 76 shows a map of deforestation hotspots in Madre de Dios in 2017, based on early warning forest loss data. The colors yellow (low), orange (medium/high), and red (very high) correspond to the areas with the highest concentration of alerts, i.e. the main deforestation hotspots of 2017. Note how the majority of the forest loss is concentrated along the recently paved Interoceanic highway.
Next, we show satellite imagery for 7 hotspots (Insets A-G) that together account for the deforestation of 6,000 hectares (15,000 acres). We show that the main deforestation drivers are gold mining and small-scale agriculture.
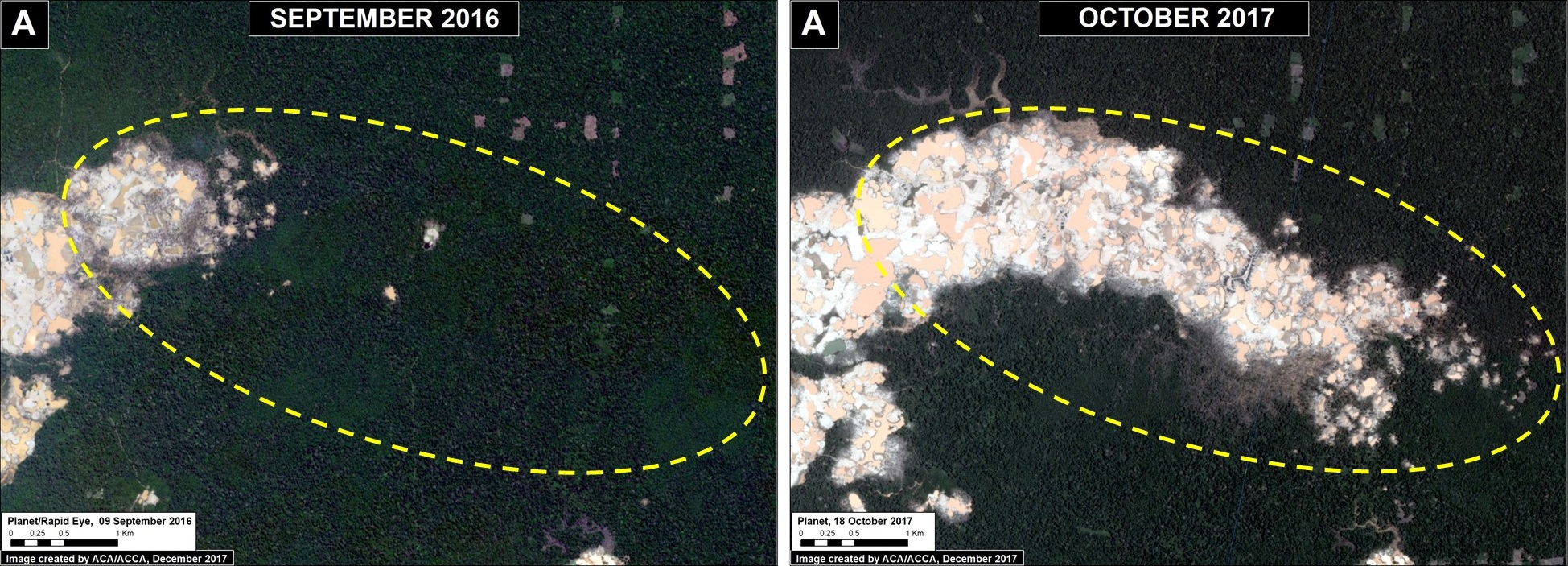
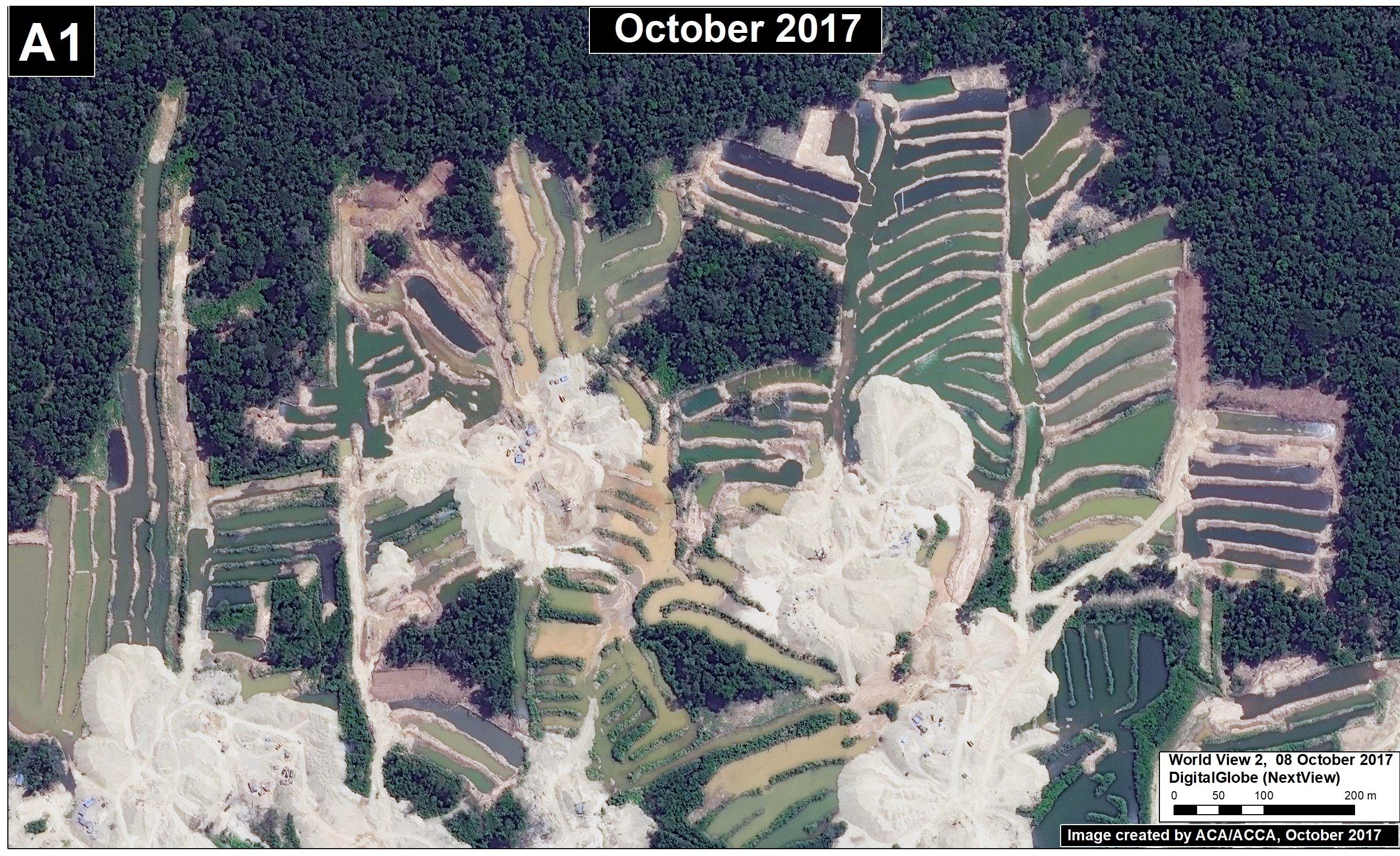
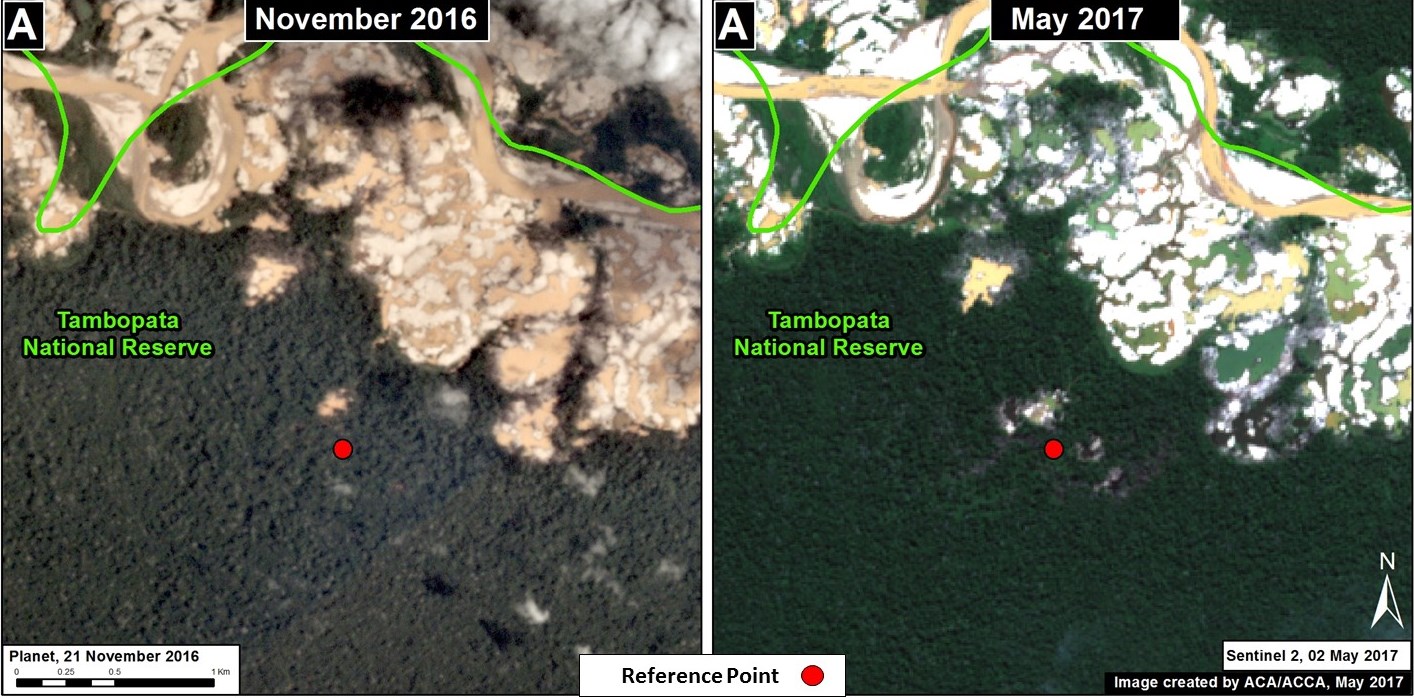
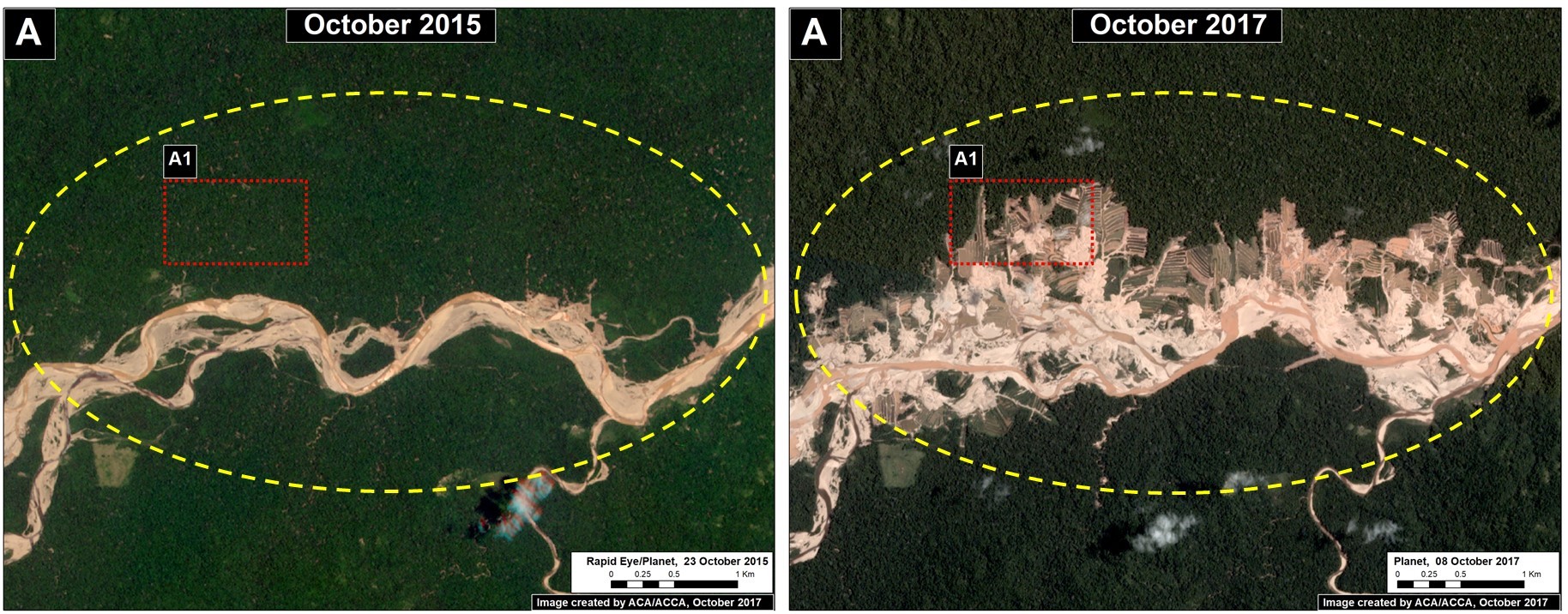
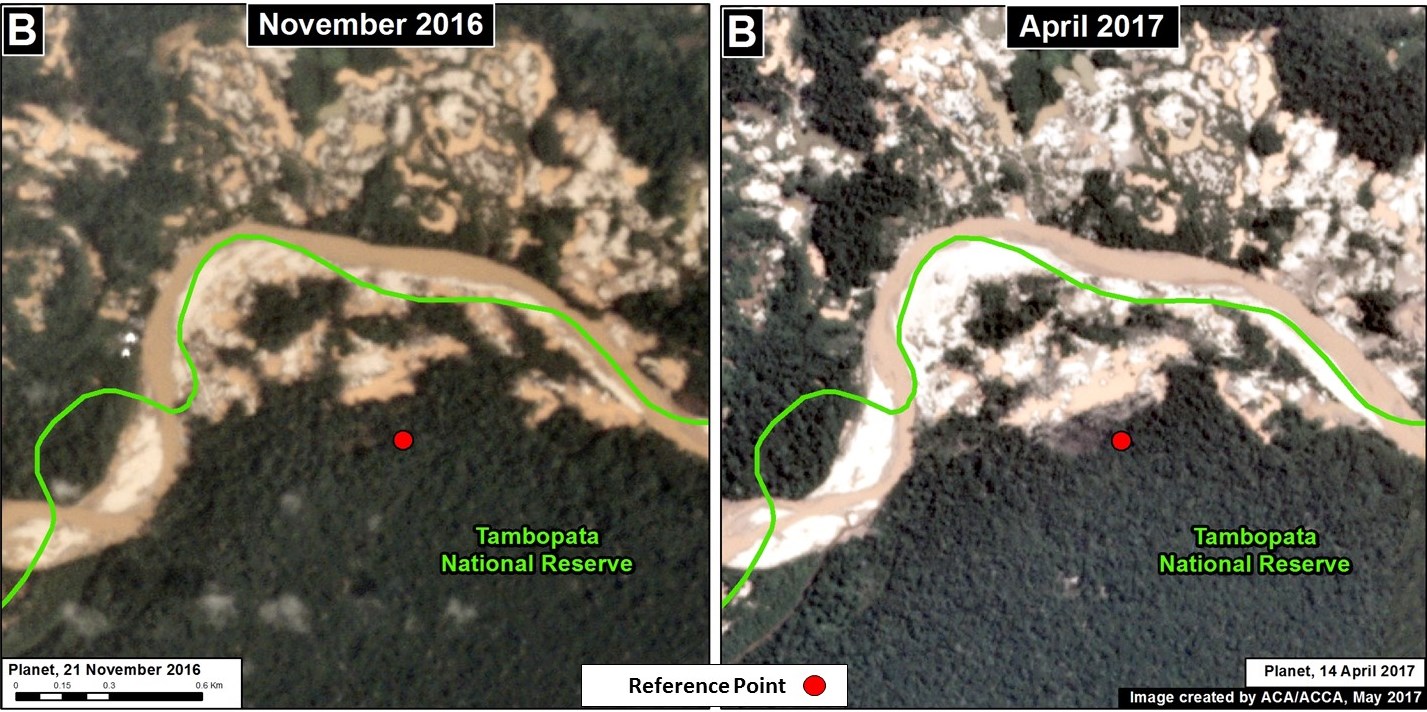
La Pampa (Inset A)
The area known as La Pampa continues to experience significant deforestation due to the advance of gold mining. Despite a series of field interventions by the Peruvian Government, we documented the deforestation of 1,385 acres (560 hectares) in 2017 (Image 76a). Since 2013, the total deforestation in La Pampa is 11,270 acres (4,560 hectares).
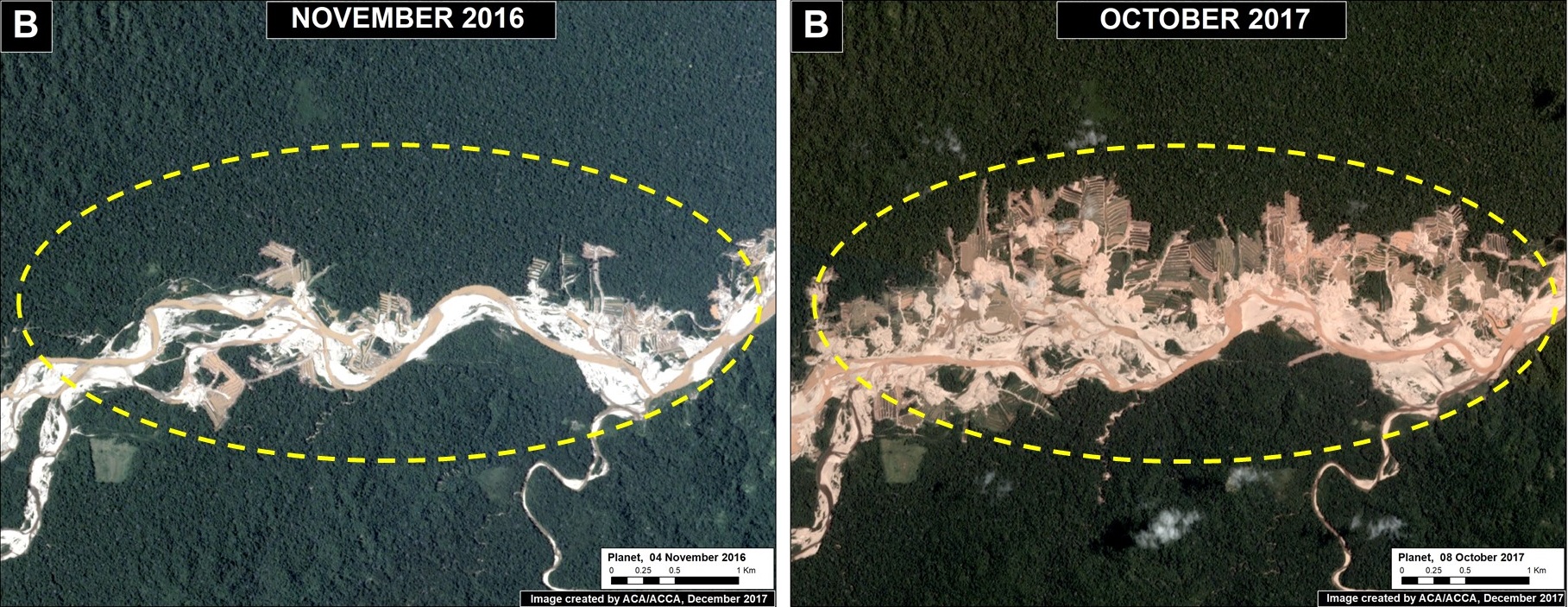
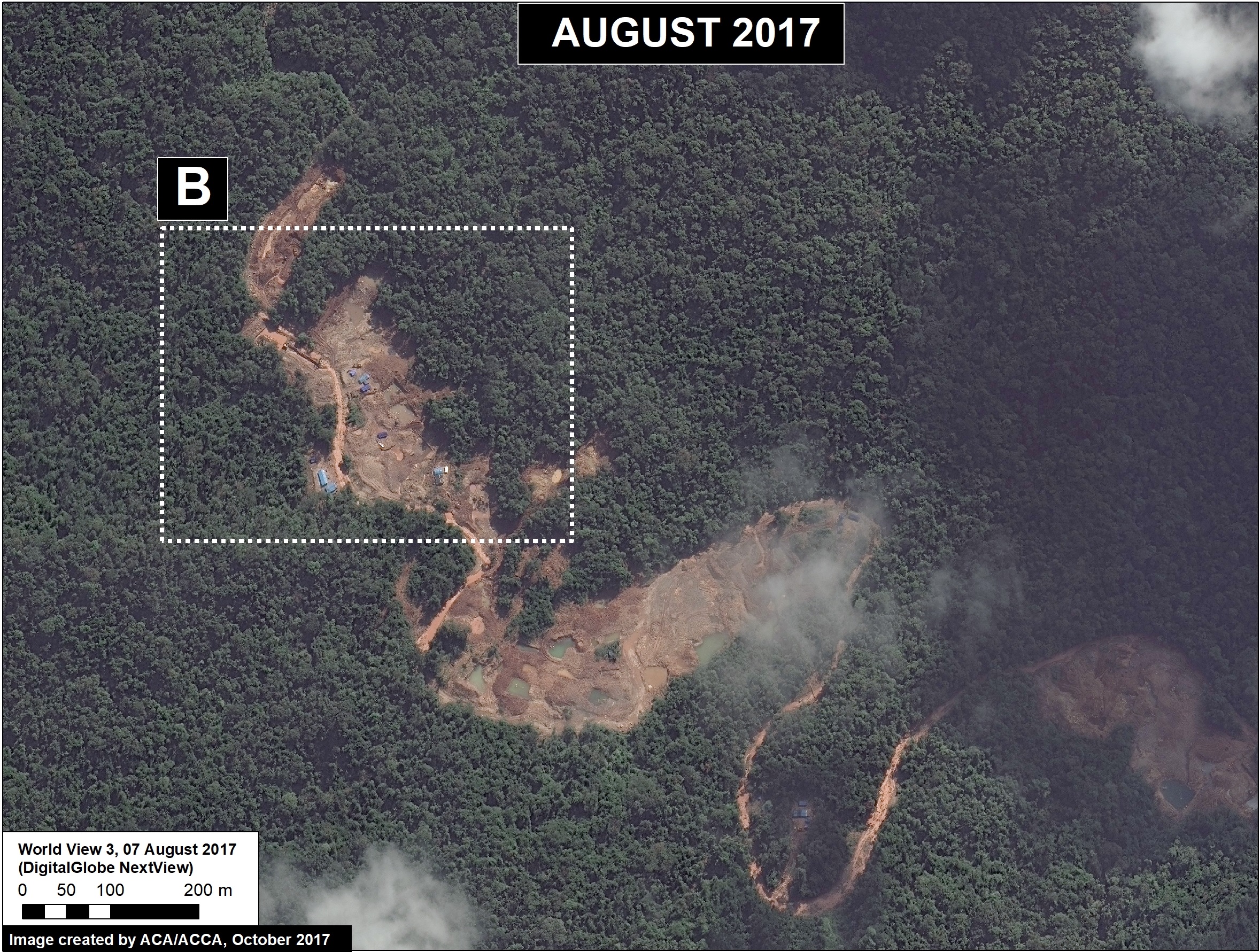
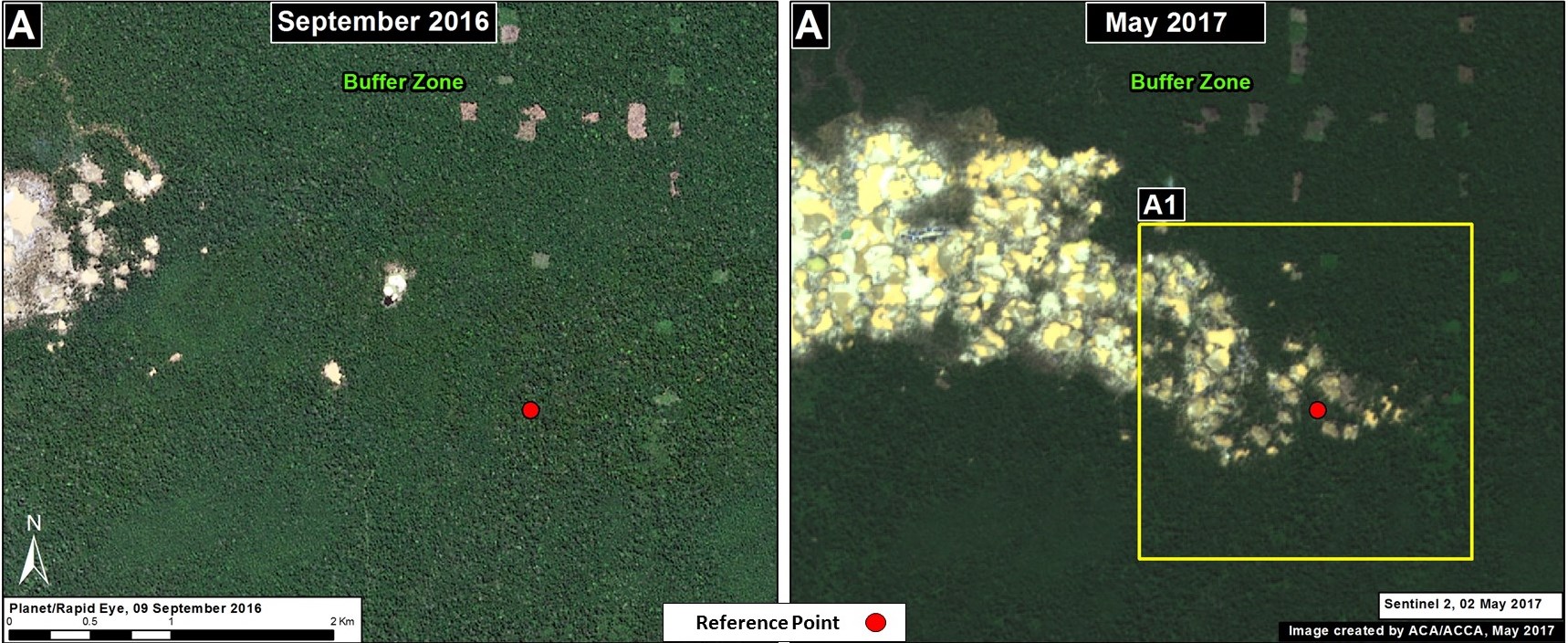
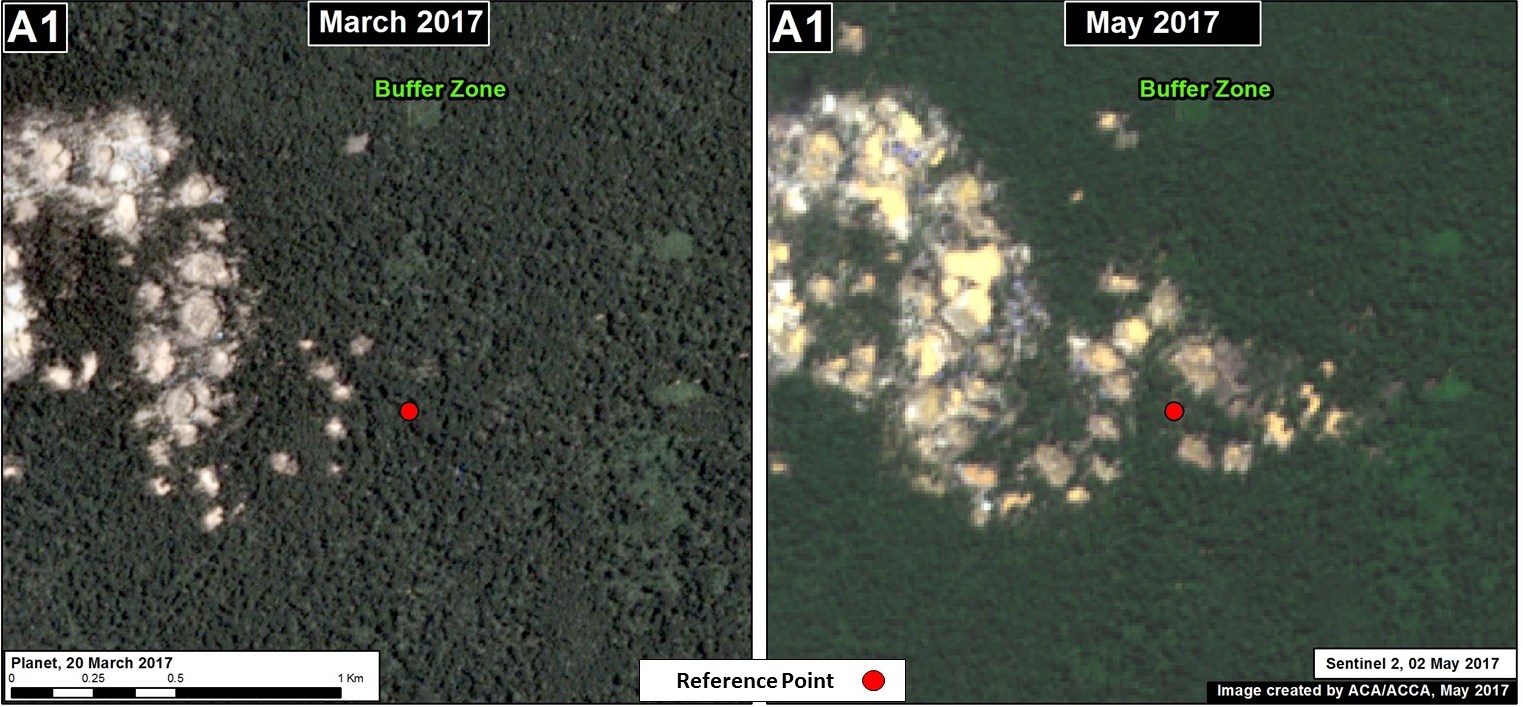
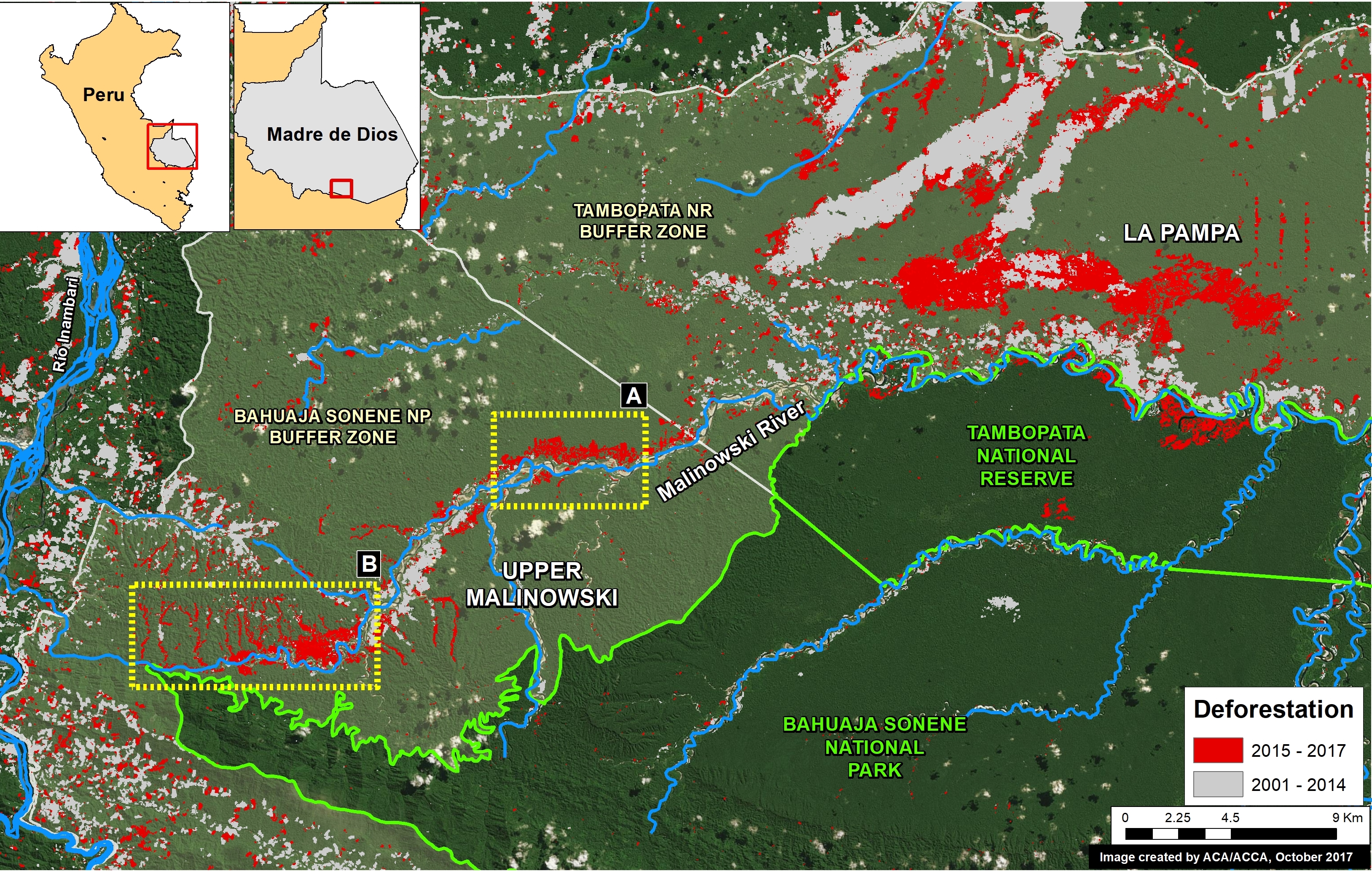
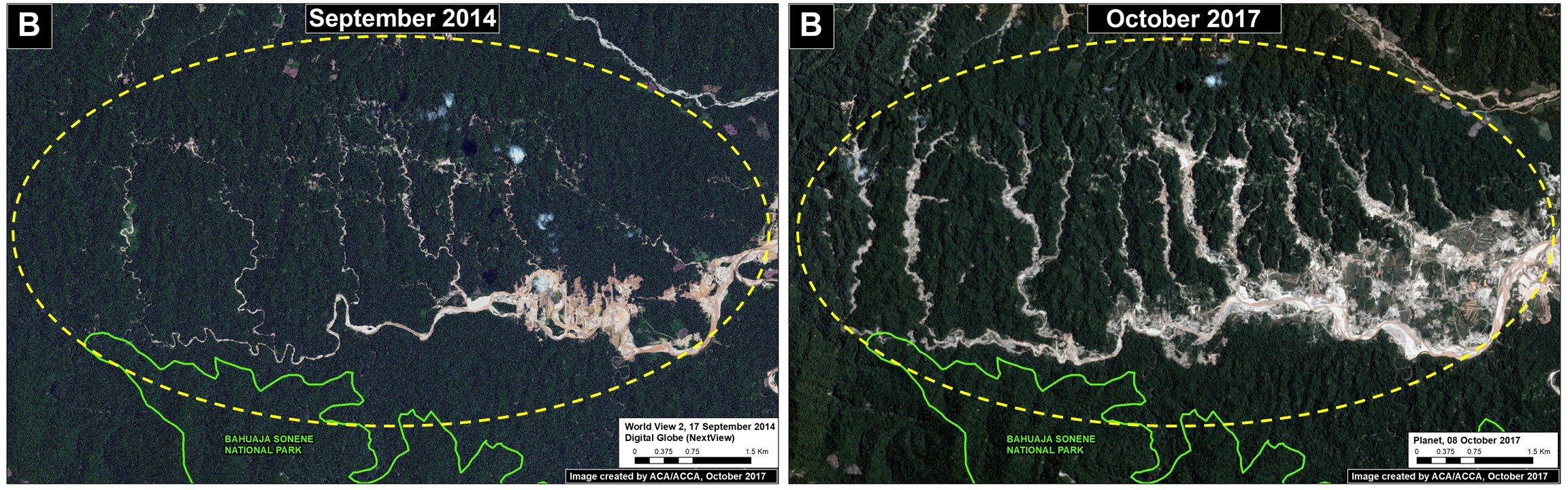
Upper Malinowski (Inset B)
Upstream of La Pampa, the headwaters of the Malinowski River represent a second area devastated by the recent advance of gold mining. We documented the deforestation of 1,795 acres (726 hectares) in 2017 along the upper Malinowski (Image 76b). Since 2015, the total deforestation along the upper Malinowski is 5,260 acres (2,130 hectares).
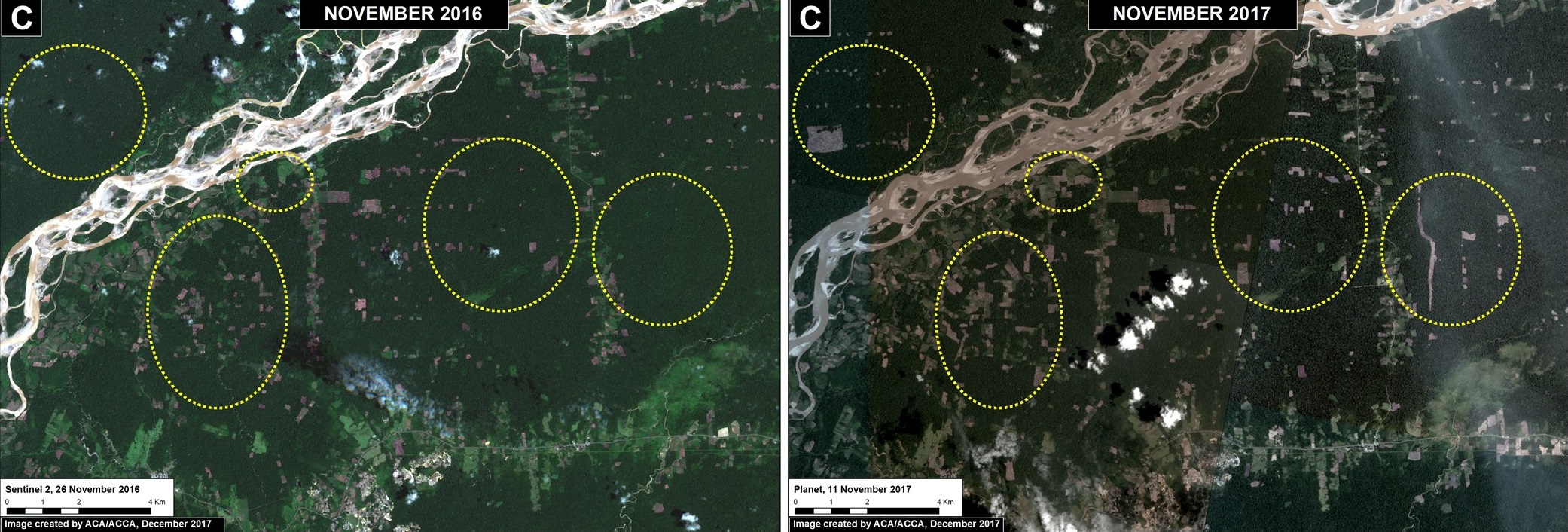
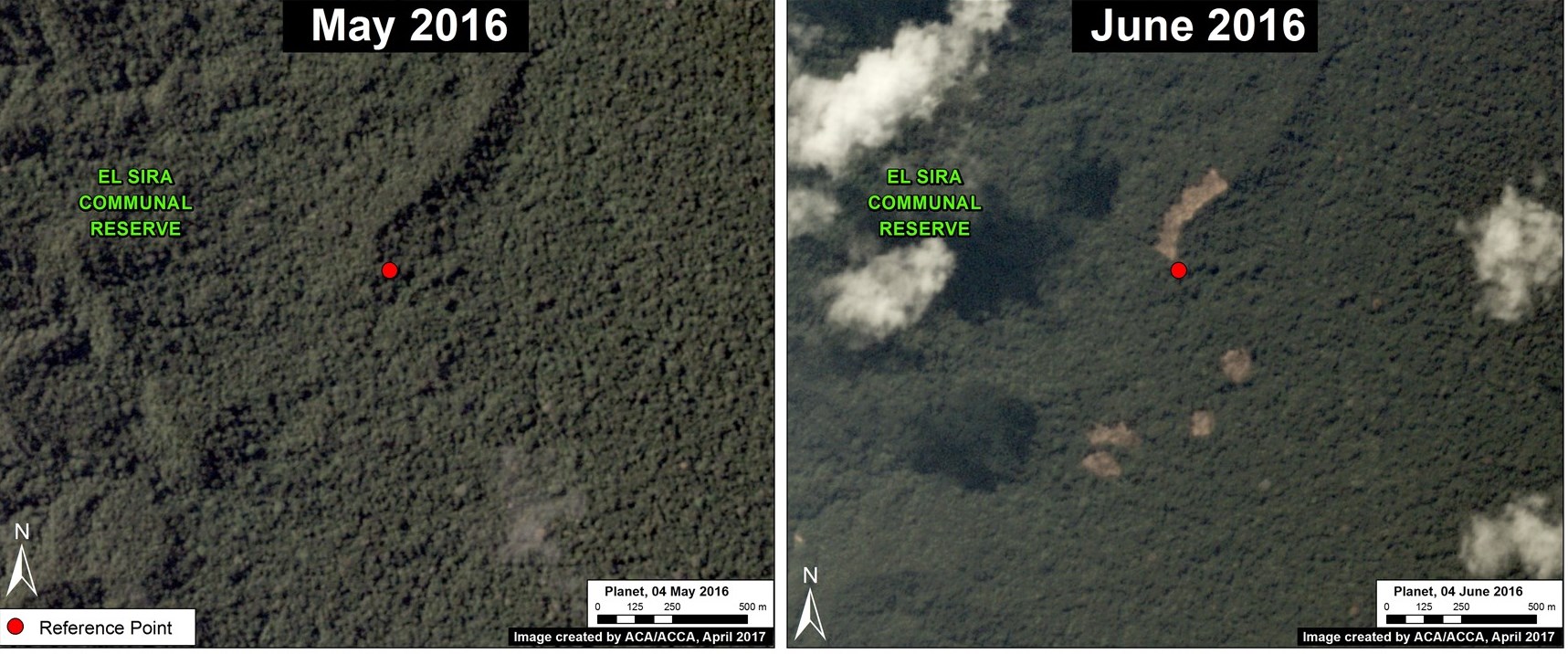
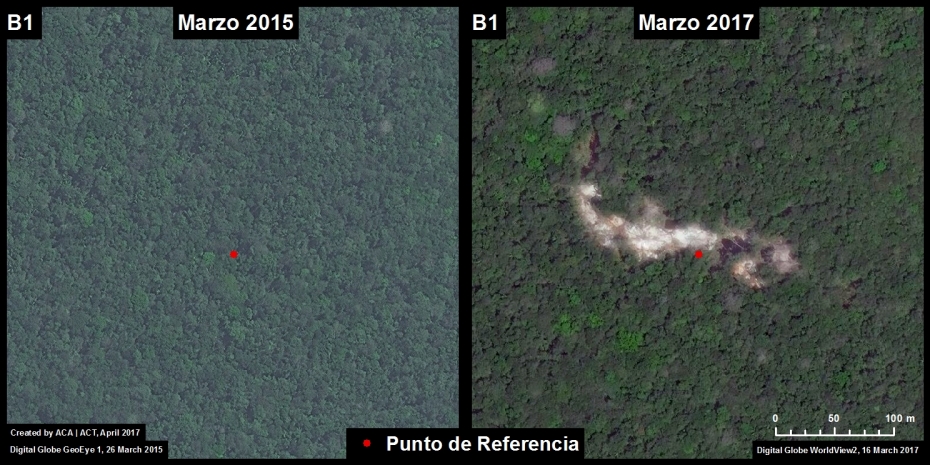
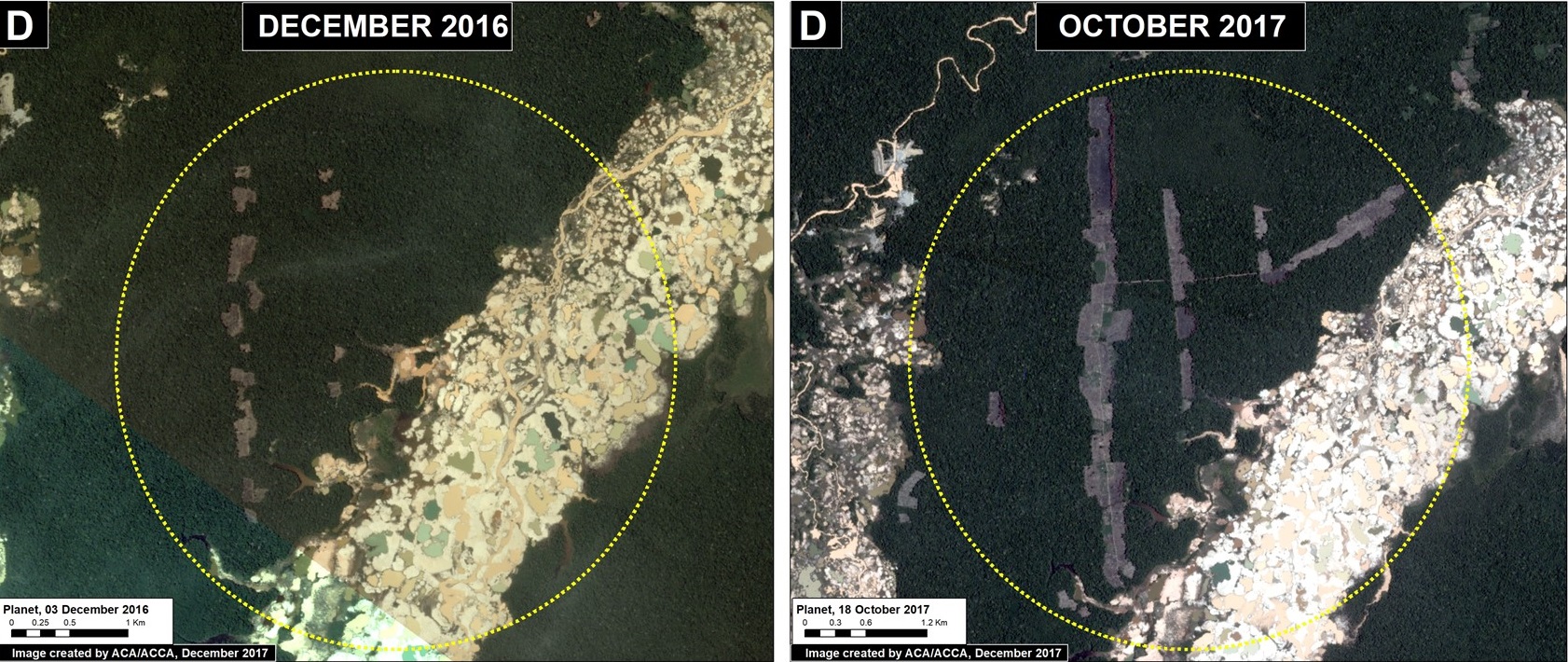
Santa Rita and Guacamayo (Insets C y D)
To the north of the La Pampa and Upper Malinowski mining areas, and on the other side of the Interoceanic highway, are two areas with significant recent deforestation due to small-scale agriculture. In these two areas, we documented the deforestation of 2,890 acres (1,170 hectares) in 2017 (Images 76c, 76d). Additional research focused on the exact type of crops is required, but local sources indicate an increase in papaya and cacao in the area.
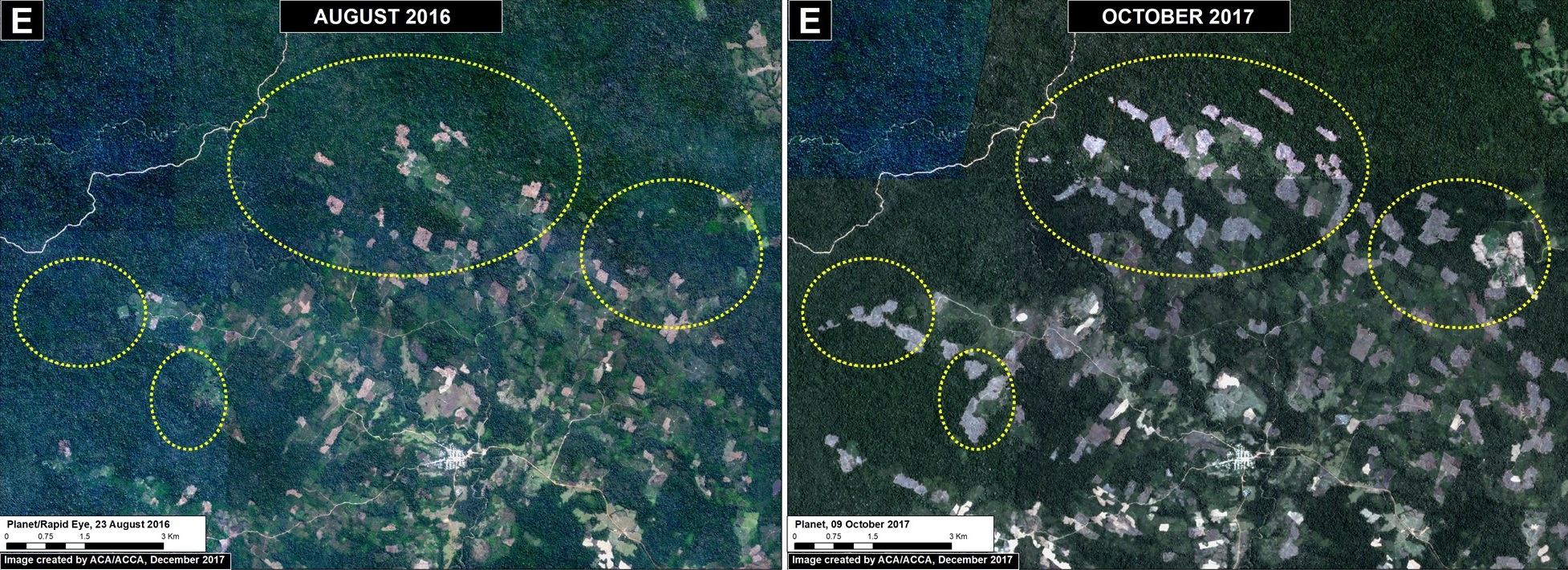
Iberia (Inset E)
On the other side of Madre de Dios, along the Interoceanic Highway near the border with Brazil and Bolivia, is the town of Iberia. This area has become a major deforestation hotspot in recent years. We documented the deforestation of 2,250 acres (910 hectares) in 2017 (Image 76e). Since 2014, the total deforestation around Iberia is 6,795 acres (2,750) hectares. A large part of the deforestation is within forestry concessions, indicating that these concessions have been invaded. The cause of the deforestation is small-scale agriculture (specifically, according to local sources, corn, papaya, and cacao).
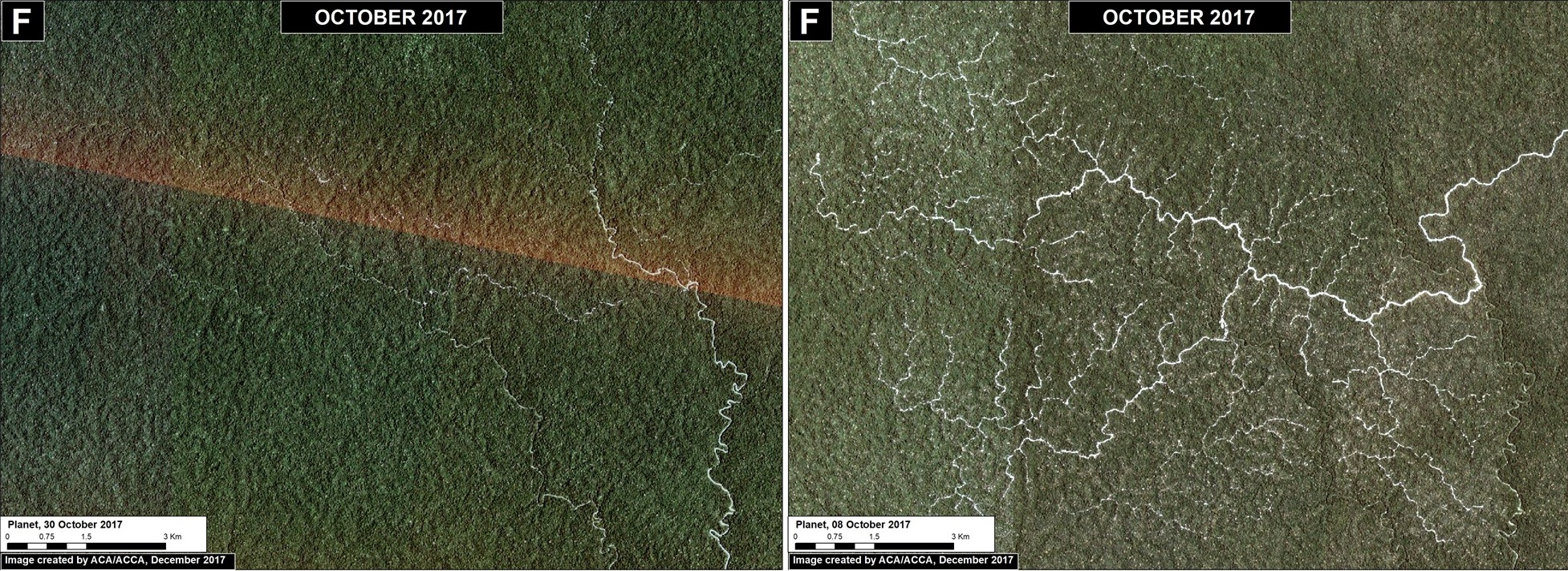
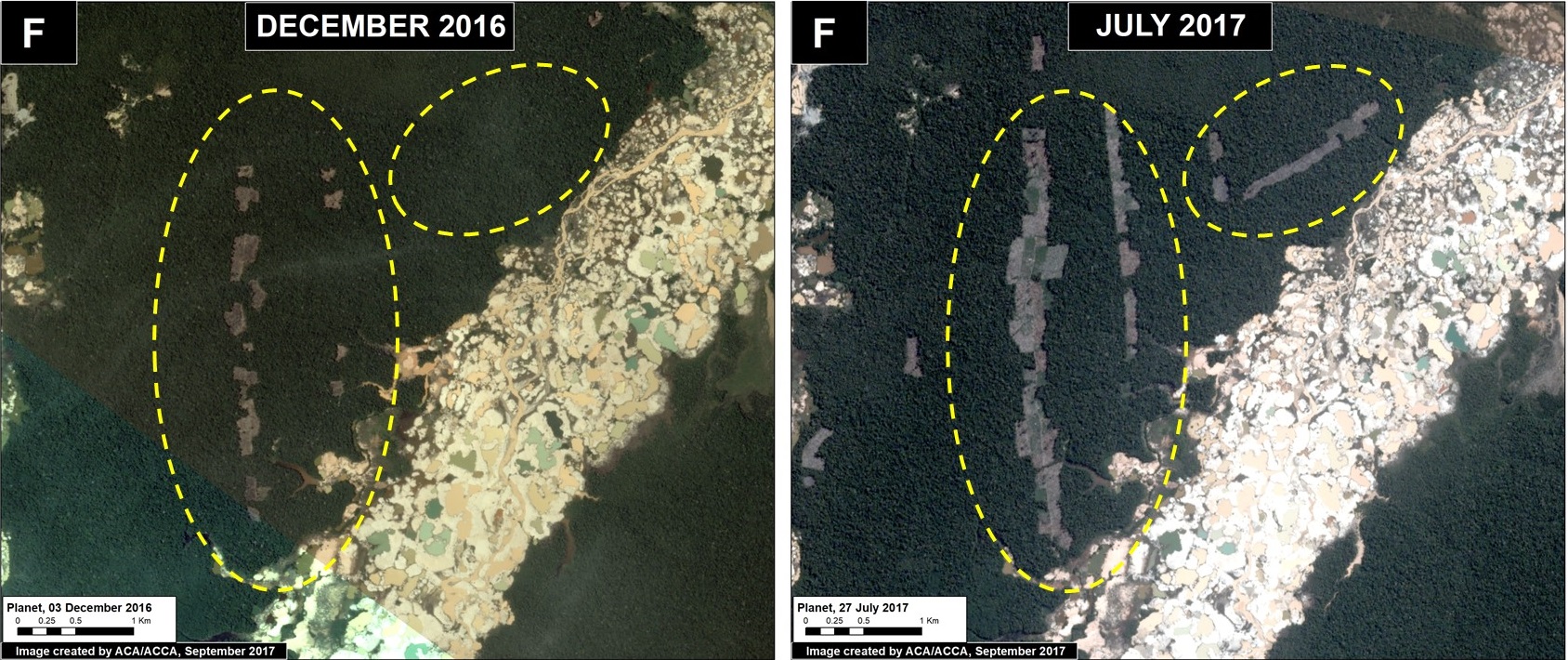
Tahuamanu (Inset F)
To the west of Iberia, an isolated hotspot emerged caused by the rapid proliferation of logging roads. This hotspot is located within a forestry concession, but its impact is troubling due to the extension and density of the new road network. We estimate the construction of 130 km of new logging forest roads in this area in 2017 (Image 76f).
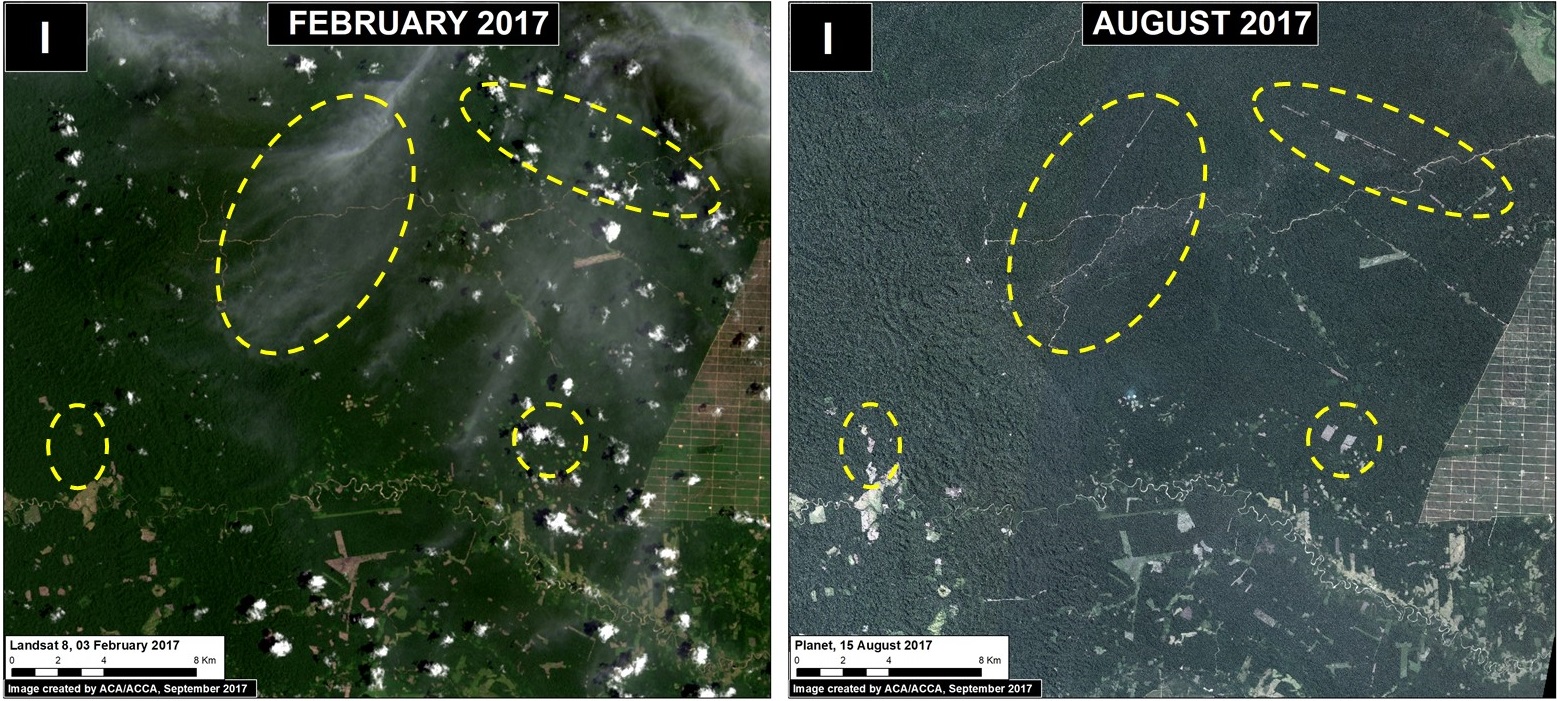
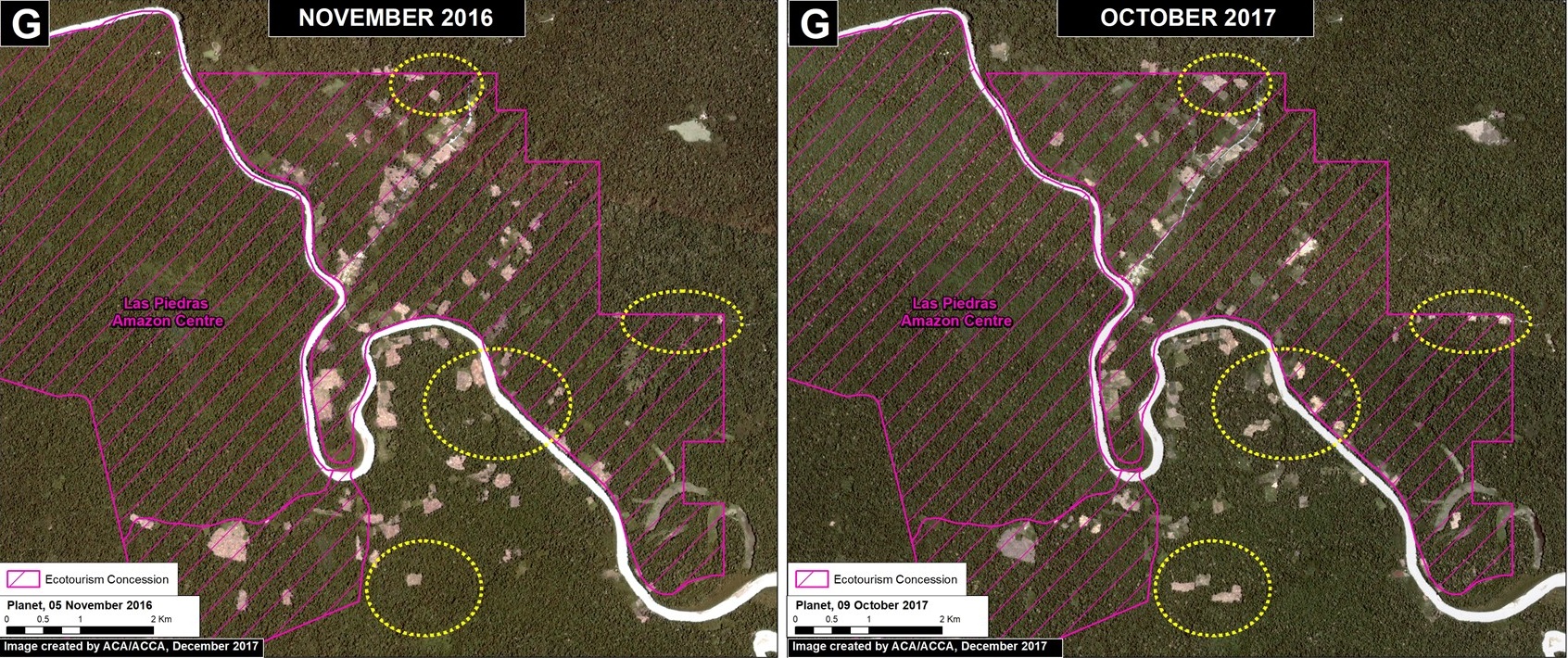
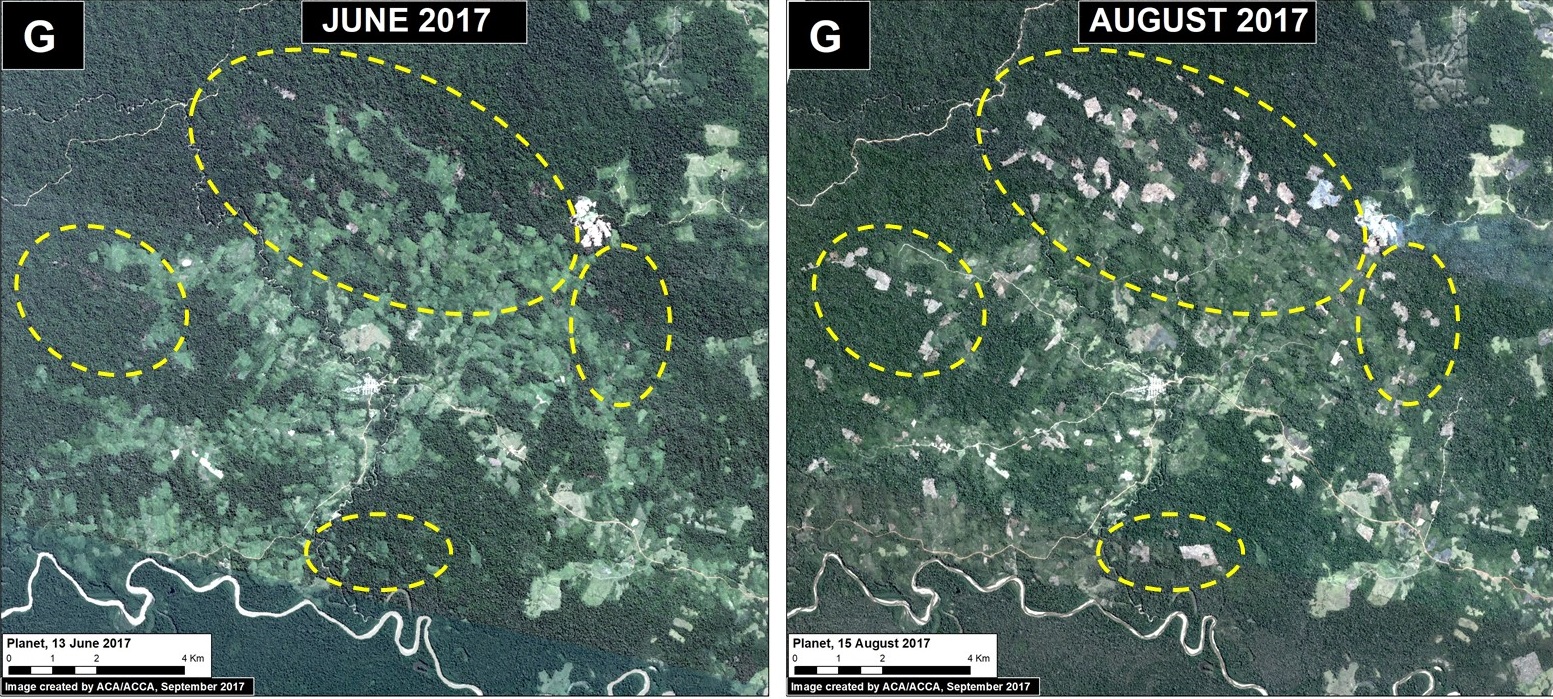
Las Piedras (Inset G)
Finally, deforestation continues within two ecotourism concessions along the Las Piedras River, a remote area famous for its exceptional wildlife (see this video). We documented the deforestation of 300 acres (134 hectares) in 2017 (Image 76g). Since 2013, the total deforestation along the Las Piedras River is 1,495 acres (605 hectares). Note that the Las Piedras Amazon Center Ecotourism Concession represents an effective barrier against deforestation impacting the surrounding concessions. According to local sources, the main causes of deforestation are cacao plantations and cattle pasture.
Coordinates
Zona A: -12.99, -69.90
Zona B: -13.05, -70.17
Zona C: -12.85, -70.26
Zona D: -12.84, -69.99
Zona E: -11.31, -69.61
Zona F: -11.23, -70.05
Zona G: -11.601711, -70.477295
References
Planet Team (2017). Planet Application Program Interface: In Space for Life on Earth. San Francisco, CA. https://api.planet.com
Citation
Finer M, Novoa S, Garcia R (2017) Pope to visit Madre de Dios (Peru), region with Deforestation Crisis. MAAP: 75.